Lecture 12: Joints Of Lower Extermities I Flashcards
(81 cards)
The nerves innervating the periarticular tissues - somewhat misleading called ___________ nerves - are composed of both postganglionic autonomic (sympathetic) and sensory axons, the latter of which end peripherally as encapsulated or free sensory receptors
Articular
Nerves to any one particular joint always arise from where?
More than one level in the spinal cord
The synovium contains a large number of what?
Thinly myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers
What are the 2 types of synovial fibers?
1) Postganglionic sympathetic adrenergic fibers -> located around blood vessels and are responsible for the control of articular blood flow 2) Unmyelinated C fibers -> responsible for pain transmission
When do unmyelinated C fibers fire?
Typically only when there is trauma -> they are nociceptive
__________________ associated with inflammation can induce signaling in the nociceptive fibers of the synovium causing pain in the normal ROM
Prostaglandin E2
What joint type is the hip joint?
Diarthrotic ball and socket type of synovial joint
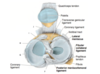
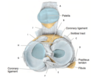
The rim of the acetabulum is incomplete inferiorly. What is this bridged by?
Transverse acetabular ligament
The acetabulum has a centrally located no articular area called the acetabular fossa. What occupies this space?
A fatpad covered by a synovial membrane -> the malleable nature permits positional changes of the femoral head during hip joint movements
In the hip joint, what deepens the socket for the femoral head?
Acetabulum depth increased. By fibrocartilaginous acetabular labrum
How can an acetabular labrum tear be induced?
By twisting on a weight bearing hip
When an acetabular labrum tear occurs, the pain may become diffuse and difficult to pinpoint and it is not possible to see swelling, although the inflamed joint may become larger in volume because of an effusion due to trauma. If the pt were to feel a pinching sensation when flexing the hip by bringing the knee up the the chest, what part of the hip joint is affected?
The front of the hip joint
In the hip joint articular capsules, some deep fibers can pass circularly around the neck of the femur forming a collar around the neck the helps hold the femoral head in the acetabulum. What is this zone called where the fibers pass circularly around the neck??
The orbicular zone
What hold down the retinacular arteries in the hip joint?
Some deep longitudinal fibers that form a retinacula superiorly along the neck
What are thickened parts of the fibrous (articular) hip joint capsule called?
Intrinsic ligaments
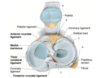
What does the iliofemoral ligament help prevent?
Overextension
What intrinsic ligament of the hip is a strong y-shaped band that covers the anterior aspect of the hip?
Iliofemoral ligament
What intrinsic ligament of the hip strengthens the joint capsule posteriorly?
Ischiofemoral ligament
What does the Ischiofemoral ligament help prevent?
Overextension
What ligament in the hi is a weak intracapsular ligament that has little importance in strengthening the hip joint?
Round femoral head ligament
The round femoral head ligament contains an obturator vessel. What might the function of that vessel be?
To assist in spreading synovial fluid
During what hip movements is the round femoral head ligament stretched?
When flexed thigh is addicted or laterally rotated
What is another name for the round femoral head ligament?
Ligamentum teres
What ligament of the hip can carry up to 30% of the blood supply to the femur and if torn can cause the bone to become necrotic due to loss of blood supply to the femur?
Round femoral head ligament - Does this through the obturator vessel