Lecture 6: Cartilage Flashcards
(96 cards)
What are characteristics of cartilage?
- Designed to bear mechanical stresses without distortion
- Shock absorber
- Frictionless movement at joints
- Bone growth
- Fracture repair
What 2 cell types are found in cartilage?
1) Chondroblasts -> replicating population of cells that secrete cartilaginous matric
2) chondrocytes -> maintain the matrix
What type of collagen predominates in the matrix of cartilage?
Type II
- Type I in fibrocartilage and outer perichondrium
- Elastic fibers in elastic cartilage
What 3 things make up the ground substance of the matrix of cartilage?
HA
Chondroitin sulfate
Keratan sulfate
What type of collagen predominates in fibrocartilage?
Type I
besides collagen and ground substance, what else is found in the matrix of cartilage?
Aggrecan
What types of cartilage are surrounded by perichondrium?
Hyaline and elastic
Does fibrocartilage contain a perichondrium?
No
In hyaline cartilage, chondrocytes are surrounded by territorial and interterritorial matrices containing type ____ collagen
II
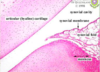
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
In embryo, articular cartilage, cartilage of respiratory tract and costal cartilage
In elastic cartilage, chondrocytes are surrounded by territorial and interterritorial matrices containing type ____ collagen AND what else?
Type II collagen and elastic fibers
Where is elastic cartilage found?
External ear, epiglottis and auditory tube
Where is fibrocartilage found?
Intervertebral disks, articular disks of the knee, mandible, sternoclavicular joints and pubic symphysis
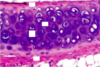
___________ is a dense CT interface around hyaline and elastic cartilage that carries the blood supply for avascular cartilage and is the source of new cartilage cells
Perichondrium
What layer of hyaline cartilage contains fibroblasts and produces type I collagen and elastin?
Outer fibrous layer
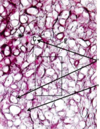
What cell type found in cartilage is often found in groups of 2-8 cells (isogenous groups)?
Chondrocytes
What layer of hyaline cartilage gives rise to chondroblasts and osteoprogenitor cells and contains chondroblasts secreting type II collagen?
Inner chondrogenic layer
What part of hyaline cartilage surrounds the isogenous cell group and contains high amounts of GAGs and lower amounts of collagen?
Territorial matrix
What part of hyaline cartilage surrounds the territorial matrix and contains more collagen II and fewer proteoglycans?
Interterritorial matrix
What location of hyaline cartilage is the exception in which it is not surrounded and nourished by a perichondrium?
Articular surfaces
Which zone of bone contains primitive hyaline cartilage responsible for the growth in length of the bone as erosion and bone deposition advance into this zone?
Reserve zone
Which zone of bone contains proliferating chondrocytes that align as vertical and parallel columns?
Proliferative zone
What zone of bone is characterized by apoptosis of chondrocytes and calcification of the territorial matrix?
Hypertrophic zone
What zone of bone is characterized by blood vessels penetrating the transverse calcified septa and carry osteoprogenitor cells with them?
Vascular invasion zone