Lecture 2: Connective Tissue Flashcards
(56 cards)
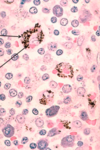
What type of CT is the arrow pointing at?

Loose
What structures does this CT make up?

Tendons
What structures does this type of CT make up?

Ligaments
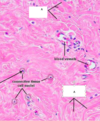
Label the arrows in this image of CT

Arrow on right = fibroblasts
Arrow on top left = collagen fibers
Next = elastic fibers
Next = Mast cells
Bottom arrows = ground substance

What type of CT is this and what type of structure does this make up?

Dense regular CT; fascia
Label the arrow in this image of CT

Fibrocyte nuclei
What type of tissue is this?

Reticular CT
What type of tissue is this?

elastic CT
What is this a picture of and what is its tissue type?

Tunica adventitia of the aorta; elastic CT
Label the arrows in this image of adult CT

Top = collagen fibers
Bottom = fibroblast nuclei

What cell type is depicted in the picture?

Macrophages
What cell type is depicted in the image?
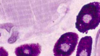
Mast cells
What cell type is depicted in the image?
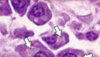
Plasma cells
Label the arrows

Top = adipocyte
Bottom = lipid
What cell type is depicted in the picture?

Fibroblasts
What cell type is depicted in the picture?

Mesenchymal cells
Undifferentiated mesenchymal cells can differentiate into what 2 things?
Blood or CT cell
What tissue type is depicted in the picture?

Dense irregular CT
What type of CT is found in the mucosa and submucosa of various organs, surrounding blood vessels, nerves and muscles?
Loose
What type of CT is found in tendons, ligaments, the cornea and fascia?
Dense Regular
What type of CT is found in the dermis and submucosa of the GI?
dense irregular
What cell type produces reticular fibers?
Fibroblasts -> specifically reticular cells
Where is reticular CT typically found?
lymphatic tissue
Where is elastic CT typically found?
In walls of large blood vessels and ligaments