Lecture 7 notes Flashcards
(64 cards)
What will we learn today?
Sources of financing - loans The need for a cash flow statement Sources and uses of cash Preparing the cash flow statement ( indirect method) Interpreting cash flow statement
What are the main sources of finance?
Owners equity
Loans/borrowings
What are long term finances in a limited company?
Share issues
Retained earnings ( internally generated profits)
Long term loans.
What are 4 types of long term borrowings?
Bank loans ( secured e.g. mortgage or unsecured)
Bonds
Debentures
Finance leasing
What does a secured bank loan mean?
“Secured” means that the lender would have the right, should the company fail to meet its interest and/or capital repayment obligations, to seize a specified asset of the business (probably some land) and use it to raise the sums involved.
What is another word for a specified asset of a business?
Collateral
What is a unsecured loan?
regular loans, you don’t have to give asset, the amount of loan given is usually lower than secured.
How are bonds a source of long term borrowings?
They can be converted into actual shares within the money. e.g. lets say we want to raise 2 million, individuals pay 2 million, in return they get a piece of paper saying you are owner of some bond, in the stock market, they get dividends and can resale their shares, in the bond market, also you get interest.
How are debentures a source of long term borrowing?
TBA
Give an example of financial leasing?
for example, a company wants to buy a large asset, when a airline company wants to buy an aeroplane, it doesn’t buy an aeroplane outright, there is a 3rd party company which buys the aeroplane, the airline company pays financial leases to this third party company, and can put this aeroplane as a non-current asset on their balance sheet. This is because these assets are expensive, it makes yearly payments to finance these.
What are 3 advantages of issuing loans instead of shares?
- Shareholders’ control is not affected
- Interest on loan is deductible for tax purposes; dividends on shares are not
- Earnings per share (EPS) may be higher (lower cost of debt)
What does it mean that shareholders control is not affected?
When you sell shares you bring in more owners but if you sell bonds or take loans then shareholder control not lost.
What does it mean that interest on loan is deductible for tax purposes, dividends on shares are not?
If you pay 10000 as interest of loan the amount is not taxed, so you can reduce it from tax amount.
What does it mean Earnings per share (EPS) may be higher (lower cost of debt)?
cost of debt means that the returns that people who issue loans except, typically loans are cheaper to take than shares, as shareholders except firm to do really well, hence higher shares.
What are 3 disadvantages of Long term loans?
o Interest must be paid on a periodic basis.
o The principal value of the loan must be paid at maturity. ( if you fail to pay this then you are forced to declare bankruptcy)
o A company with volatile earnings and a relatively weak cash position (e.g. weak liquidity) may face great difficulties making interest payments when earnings are low.
Assume ABC takes up a 5 year loan of £100000 with an interest rate of 5% . What is the double entry for this?
Dr Cash £100000
Cr Loans £100000
Repayment By the 31st of December 2010, ABC has made a repayment of 22,000, (repayment of principal £15,000, interest £7,000). What is the double entry for this transaction?
Dr interest expense - 7000
Dr loan - 15000
Cr Cash £22000
As an investor why would you pick bonds?
1) Interest is a legal obligation, and loans have priority in repayment ( even if they go bankrupt they get their money)
As an investor has I know that i will always get my money back and interest what does this mean about returns?
The returns are lower than shares and less risk.
As a investor why would you pick buying shares?
Despite dividends not being a legal requirement and if their is any residual profit left they get their contribution last, they get the benefit that if the value of the share goes up and sell their share. Thus ordinary shares are more risky form of investment but could lead to higher returns.
Why do companies issue Equity ( shares)
1) When issuing equity ( this signals that you have a higher quality company, as you are allowing investors to judge your company).
2) Shareholders have residual claim on cash flows
3) Dividends are not a legal requirement and principal amount has to be paid)
So conclude why do companies issue equity?
It offers a more flexible form of financing.
So how does a firm choose whether to issue debt or equity?
Depending on current situation, firms will evaluate which one is better for them, e.g. firm is not doing well, they will choose to issue shares as they will not be able to repay loan amounts, if firm is doing well, then they might take some amount of loans.
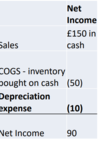
What does the cash flow statement denote?
From where did the cash come in How did we use the cash Where did the cash go out How much cash remains in firm, at the end of the period.