Lecture 9 notes Flashcards
(60 cards)
What will we learn today?
How to account for mergers and accquistions
Why do firms accquire other firms?
Growth by accqusition
diversification
Take advantage of limited liability
Vertical and horizontal intergration
Synergies = EOS and scope
What does horizontal intergration mean?
eliminate/reduce competition i.e google did this.
What does vertical intergration mean?
accquire new sources of supply ( e.g. lets say you have a supplier and they do not provide things on time, thus you think its time to make your supplier chain better, hence you accquire a supply chain yourself, accquiring another firm in the same industry.
What does diversification mean in the context of firms accquiring other firms?
if you want to move into a new industry but don’t have an established prescence in the industry, what you do is you accquire and established firm and diversify in a different operation.
What does taking advantage of limited liability mean?
(If there is a financial failure of one subsidiary, neither the assets of other subsidiaries nor those of the parent could be legally demanded by any unsatisfied claimants (such as lenders) )
What is a Parent or holding company?
Company that owns the shares of the ‘subsidiary’ company.
What is a subsidary?
Company whose sharees are partly or wholly owned by the parent.
What does the parent have to show their shareholders, with their accquistions?
A consolidated B/S of the parent and subsidary together, presenting an overview to investors of whole group.
A consolidated I/S to.
They do not care about internal transcations.
What are 3 types of group structures that parent companies are in?
1) Parent accquiring one subsidary
2) Parent accquiring many subsidaries e.g. 4
3) Indirect control
What is the group structure of a Parent accquiring subsidary?
The parent creates a new company to operate some part of its business. For example, the would-be parent company forms a new company to undertake the work that has previously been done by the parent’s industrial division.

What is the group structure of parent having multpile subsidaries?
The parent has multpile subsidaries e.g. 4 in each, they have atleast 50% direct holdings, or control of atleast 50%, this means that you can for example have voting rights. ( change CEO)

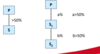
What is the group structure of indirect control?
Here the Parent owns 1 and 3 directly but 2 indirectly, It has majority shareholdings in 1, thus it means in 2.

What does control mean in terms of Parent owing a subsidary?
The power to govern the financial and operating policies
Control is presumed when P owns more than 50% of the voting rights of S.
Is it possible that the parent can have less than 50% and still have control of S?
yes it is possible, through an agreement, allowing the parent company to change policies etc. ( e.g. big pension fund investing in sainsburys, this pension fund owns ownly 40%, but through some agreement, they have given this pension fund voting rights, thus the pension fund has control)
What happens when the parent company has control over the subsidary?
When P has effective control over S, P needs to prepare consolidated financial statements (or group accounts) as if the group was a single entity. ( e.g. M&S create a subsidary called M&S clothing , you the investor are shareholders of M&S, so you are interested in how well the parent is doing as well as the subsidary.
Why does the parent company make consolidated B/S for investors in parent?
Lets say the parent receives some dividend income from the subsidary and the parent has paid money to accquire the subsidary. To the investors of the parent, these look like internal transcations, these shareholders do not care about internal transcations, they care about how the group as a whole perfoms, in relationship to external world.
So it is important to remove any internal transcation that have occured, whilst consolidating.
To prepare for consolidated balance sheet she are going to look at how many cases?
7
What is the first case we will look at when creating a consolidated balance sheet?
1) Case 1: P(parent) accquires 100% of Subsidary equity
Give an example of case 1?
Assume Parent (P) acquires 100% of Subsidiary (S)’s equity for £100m
- Investment in S = £100m
- P acquires S’s equity = assets – liabilities (net assets) = £80m (the parent gets the equity secton) Why pay more than its net assets’ worth?
Market premium = £20m
What is Market premium of 20m also known as?
Goodwill.
When preparing consolidated b/s for the simple case 1 what do you do?
You first ADD
then elimanate Equity of Subsidary and Investment in S ( entire equity section of S), AS these look like internal trasncations to the outside shareholder, so you cancel this out, but this only happensn when you pay the exact amount for the firm as the equity section
When you pay more for the firm, whatever extra you pay, you note down as Goodwill which is a non current asset, as the benefit will be long term.

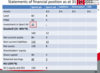
Sprint plc bought 100% of the shares of Sport Ltd on 31 December 2011 for a consideration (purchase price) of £10 million. The statements of financial position of the two companies as of 31 Dec 2011 are as follows: How would CBS look like?

1) You add like items, you remove investment in subsidary and equity section.
2) Calculate the good will ( you paid 10 and got the equitiy section so goodwill is 2.)

What are the benefits that arise from Goodwill?
Cost synergies
Sales syneries ( technological and innovative skills)