Module 1.1 Flashcards
(29 cards)
Tissue
a group of similar cell specialized in a common direction and able to perform a common function
What are the four basic tissue types?
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
Nervous
Describe epithelial tissue
Closely apposed cells with very little intercellular substance between them, arranged in sheets to either cover or line surfaces of the body or to form glands
What are the 6 special characteristics of epithelial tissue?
- cellularity
- polarity
- special contacts
- supported by connective tissue
- Avascular but innervated
- regenerative
What are the three surface variations of epithelia?
- plain
- cilia
- microvilli
What is the function of cilia?
propels substances over surfaces
What is the function of microvilli?
increase exposed surface area
How are endocrine glands formed?
they are an outgrowth of the epithelial layer
What is the function of exocrine glands?
excrete to epithelial surface
What is the function of endocrine glands?
release into capillary
Describe simple squamous
a single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped central nuclei and sparse cytoplasm
What is the function of simple squamous?
allows passage of materials b diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important; secretes lubricating substances in serosae
Where is simple squamous located?
- kidney glomeruli
- air sacs of lungs
- lining of the heart
- blood vessels
- lymphatic vessels
- lining of ventral body cavity
Identify the cell type decticted
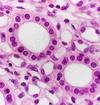
Describe imple cuboidal
What is the function of simple cuboidal
secretion and absorption
Where is simple cuboidal located?
- kidney tubules
- sucts and secretory portions of small glands
- ovary surface
Identify the cell type
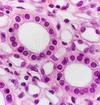
Describe simple columnar
single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei; some cells bear cilia
What is the fucntion of simple columanr?
absorption; secretion of mucous, enzymes and other substances; ciliated type propels mucous by ciliary action
Where is simple columnar located?
nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract, gallbladder and excretory ducts of some glands; ciliated variety lines small brinchi, uterine tubes and some regions fo the uterus
identify the cell type
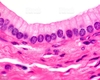
Describe stratified squamous
thick membrane composed of several cell layers; basal cells are cuboidal or columnar and metabolically active; surface cells are flattened; in the keratinized type, the surface cells are ful of keratin and dead; basal cells are active in mitosis and produced the cells of the more superficial layers
What is the fucntion of stratified squamous?
protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion




