Peripheral Nervous System Flashcards
(53 cards)
Define “ganglion”
A cluster of cell bodies outside of the CNS; enveloped in an epineurium

Describe the dorsal root ganglia
Ganglia a short distance away from the spinal cord; contain neurosomas (cell bodies) of sensory neurons

Describe the sympathetic ganglia
Neurosomas that lie laterally to the vertebral body; responsible for carrying motor information

Name the twelve cranial nerves

I: Olfactory
II: Optic
III: Oculomotor
IV: Trochlear
V: Trigeminal
VI: Abducens
VII: Facial
VIII: Vestibulocochlear
IX: Glossopharyngeal
X: Vagus
XI: Accessory
XII: Hypoglossal

Describe cranial nerve I. Name? Function? Origin? Termination?
Name: Olfactory nerve
Function: sensory; contains “fascicles”, or projections from the olfactory bulb through the ethmoid bone into the nasal cavity
Origin: Olfactory mucosa in nasal cavity
Termination: Olfactory bulb

Describe cranial nerve II. Name? Function? Origin? Termination?
Name: Optic nerve
Function: Sensory; responsible for relaying visual information from the retina to the thalamus and midbrain at the optic chiasm; ultimately leads to occipital lobe
Origin: Retina
Termination: Thalamus and midbrain

Describe cranial nerve III. Name? Function? Origin? Termination?
Name: Oculomotor
Function: Predominantly motor responsible for opening of eyelid, pupillary constriction, and focusing
Origin: Midbrain
Termination: somatic fibers to levator palpebrae superioris; superior, medial, and inferior rectus muscles, and inferior oblique of the eye; autonomic fibers enter eyeball and lead to constrictor of iris and ciliary muscle of lens

Describe cranial nerve IV. Name? Function? Origin? Termination?
Name: Trochlear
Function: Predominantly motor; responsible for medial eye movements
Origin: Midbrain
Termination: superior oblique muscle of contralateral eye

Describe cranial nerve V. Name? Function? Subdivisions?
Name: Trigeminal
Function: Mixed nerve for sensation and chewing
3 divisions: V1 = opthalmic; V2 = maxillary; V3 = Mandibular

Describe subdivision V1 of the trigeminal nerve. Name? Function? Origin? Termination?
Name: Ophthalmic
Function: touch, temperature, pain, and sensation from upper face
Origin: superior region of the face; surface of eyeball; lacrimal gland; superior nasal mucosa; frontal and ethmoid sinuses
Termination: Pons

Describe subdivision V2 of the trigeminal nerve. Name? Function? Origin? Termination?
Name: Maxillary
Function: Touch, temperature, and pain from the lower face
Origin: Middle region of the face; nasal mucosa; maxillary sinus; palate; upper teeth and gums
Termination: Pons
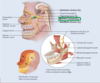
Describe subdivision V3 of the trigeminal nerve. Name? Function? Origins? Terminations?
Name: Mandibular
Function: Mixed; some sensory for the lower face; motor for mastication (chewing)
Sensory origin: Inferior region of the face, anterior 2/3 of tongue (not taste buds), lower teeth and gums, floor of mouth, and dura mater
Sensory termination: Pons
Motor origin: Pons
Motor termination: Anterior belly of digastric; masseter, temporalis, mylohyoid, and pterygoid muscles; tensor tympani muscle of inner ear

Describe cranial nerve VI. Name? Function? Origin? Termination?
Name: Abducens
Function: Lateral eye movement
Origin: Inferior pons
Termination: Lateral rectus muscle of the eye

Describe cranial nerve VII. Name? Function? Origins? Terminations?
Name: Facial
Function: Mixed; taste; facial expression; secretion of tears, saliva, nasal, and oral mucus
Sensory origin: taste buds of anterior 2/3 of tongue
Sensory termination: Thalamus
Motor origin: pons
Motor termination: somatic fibers of digastric muscle, stapedius muscle of middle ear, stylohyoid muscle, muscles of facial expression. Autonomic fibers to submandibular and sublingual salivary glands, tear glands, nasal and palatine glands

What are the five subdivisions of the facial nerve (CN VII)?
Temporal
Zygomatic
Buccal
Mandibular
Cervical

Describe cranial nerve VIII. Name? Function? Origins? Terminations?
Name: Vestibulocochlear
Function: Predominantly sensory; hearing and equilibrium
Sensory origin: cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular ducts
Sensory termination: Fibers for hearing end in medulla; fibers for equilibrium end at junction of medulla and pons
Motor origin: Pons
Motor termination: Outer hair cells of cochlea of inner ear

Describe cranial nerve IX. Name? Function? Origins? Terminations?
Name: Glossopharyngeal
Function: Mixed; senses taste, touch, pressure, pain, and temperature on tongue and outer ear; regulates blood pressure and respiration; motor controls salivation, swallowing, and gagging
Sensory origin: pharynx; middle and outer ear; posterior 1/3 (including tastebuds) of tongue; internal carotid artery
Sensory termination: Medulla oblongata
Motor origin: Medulla oblongata
Motor termination: Parotid salivary gland; glands of posterior tongue; stylopharyngeal muscle (dilates pharynx for swallowing)

Describe cranial nerve X. Name? Function? Origins? Terminations?
Name: Vagus
Function: senses taste, hunger, fullness, and gastrointestinal discomfort; responsible for swallowing, speech, deceleration of heart, bronchoconstriction, gastrointestinal secretion and motility
Sensory Origin: Thoracic and abdominal viscera, root of tongue, pharynx, larynx, epiglottis, outer ear, dura mater
Sensory Termination: Medulla oblongata
Motor Origin: Medulla oblongata
Motor Termination: tongue, palate, pharynx, and most other internal organs

Describe cranial nerve XI. Name? Function? Origin? Termination?
Name: Accessory
Function: primarily motor; swallowing; head, neck, and shoulder movements
Origin: Medulla oblongata and spinal cord segments C1-C6
Termination: Palate; pharynx; trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles
“wanna be spinal nerve”

Describe cranial nerve XII. Name? Function? Origin? Termination?
Name: Hypoglossal
Function: Primarily motor; tongue movements of speech, food manipulation, and swallowing
Origin: Medulla oblongata
Termination: Intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue

Define plexus
A network of intersecting nerve fibers that serve the same part of the body
How many PAIRS of spinal nerves are there and what are their subdivisions?
31 pairs
C1-C8
T1-T12
L1-L5
S1-S5
Co1

Describe the proximal branches of spinal nerves. Where do they emerge? What kind of nerves are they? What structures are associated with it?
6-8 rootlets emerge from the anterior surface on either side of the spinal cord to form the ventral root (and posterior rootlets form the dorsal roots)
Dorsal root ganglia lie just distal to the point where posterior rootlets converge; sensory
Dorsal and ventral roots merge just beyond dorsal root ganglion and exits the vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramen

Describe the distal branches of spinal nerves
Begin immediately after emerging from the intervertebral foramen
Divides into posterior and anterior rami as well as a small meningeal branch (detects swelling at the spinal cord)




















