Quiz 3 Flashcards
(47 cards)
The larger the gradient, the _____ the water movement
faster
Evaporation = most water loss by ______ organisms
terrestrial
What happens to the gradient as moisture is added to the air?
less pronounced
Where should evaporative coolers work best?
warm, dry climates
What is Relative Humidity?
Water Vapor Density / Saturation Water Vapor Density x 100
Amount of water vapor/ volume of air
Water Vapor Density
In the _______, the air at the surface of the planet can hold a lot of water vapor (_______ saturation water vapor density) because the air is ______ in temperature.
tropics high warm
What should a beetle do on a hot day to avoid evaporative water loss?
hide fam, just hide
Greater % water in freshwater or ocean?
freshwater
Isosmotic
same osmolarity as
Hyperosmotic
tissue has higher concentration of solute than enviornment [fish is in hypotonic solution]
Hyposmotic
tissue has lower concentration of solute than environment [fish is in hypertonic solution]
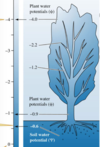
Water movement between Soils and Plants moves down a _______ ________ _______.
Water potential gradient
Water potential (Ψ(psi)) = ________
capacity of water to perform work.
Water potential relates to water’s ability/likelihood to a. evaporate b. move c. enter the roots d. all of the above
d. all of the above
in nature Ψ is usually…
negative
2 major challenges for organisms on land:
- evaporative loss
- reduced acess to replacement
Animal’s internal water (Wia) = _______ - ________
Input sources
losses
Osmosis, drinking, absorbing and metabolism are examples of what?
water gain
Root development increases with ____ water availability
low
Wide, shallow roots facilitate water collection from ________
heavy, infrequent rainfall
How do Dune plants grow vs. non-dune plants?
- both grow with water
- When unwatered, however, dune plants grew large roots, but non-dune plants show poor growth
What are the 2 ways organisms combat water scarcity?
- water acquisition
- water conservation
How do waxy tree frogs conserve water?
secrete a fatty, waterproof covering


