Technology/Innovation Flashcards
(39 cards)
How is the following produced?
Paper
- Cut and dissolve: Wood is diced into single-inch chips and cooked in an acidic solution to separate the desirable plant fibers from the undesirable lignin.
- Treatment: The pulp is cleaned and bleached with water and a calcium-based carbonate bath. The treatment causes it to acquire the white color that is characteristic of paper.
- Final steps: The pulp is flattened and allowed to dry.
Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
Transistors
Mechanism: a small signal applied between two terminals is used to trigger a larger signal between two other terminals
Function: Amplifiers (either of voltage, current, or both) or digital switches (on or off) (allow for precise control of the amount and flow of current through circuit boards)
Use: amplification for sound reproduction, radio transmission, and signal processing; switch processes for logic gates

Give a simplified explanation of how magnets work.
An element (A) with half-filled electron shells will exert a force on others like it (B) because their electrons are ‘falling’ into filled shells when A and B are together
(An explanation from a paper I once wrote for a physics course: Electrons and protons are oriented so that they have a natural spin in a certain direction (Similar to a spinning top), and the protons have a north and a south end too, just as magnets do. One way to think about magnets is that magnets are substances in which many of the spins of the subatomic particles are pointed in the same direction, and so this invisible force of the spin is concentrated in one direction.)
Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
Electromagnets
Mechanism: wire wrapped (i.e. a solenoid) around a ferromagnetic core (e.g. iron). More wrappings = stronger field
Function: temporary magnetism when a current is applied
Use: motors, generators, transformers, MRIs, etc.

Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
MRI
1. A large magnet is used to rotate/align the water-associated protons in a patient’s body by 90° (this is known as precession).
2. The protons then rotate back to the orientation of the main magnetic field. This rotation of magnetic field induces an electric current in the sensors around the patient, and, thus, an electric signal is produced
(I.e. opposing magnetic fields rotate body protons, and then the protons’ rotate and emit energy, producing electric currents that we can read as images.)
Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
Transformers
Mechanism: an electromagnetic force is generated by the initial coil; the ratio of loops in coil 1 and 2 is used to generate a higher or lower voltage using the EMF
Function: to either increase or decrease voltages
Use: to increase voltage in power lines so that resistance becomes less of an issue to energy transfer (V = IR)

Transmitters vs. receivers


Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
Semiconductors
Simply a substance with a conductance between a conductor and an insulator (e.g. silicon).
Mechanism: transfer of electrons through a crystal lattice – passing current more easily in one direction than the other, showing variable resistance, and sensitivity to light or heat
Uses: transistors; nearly all electronics
Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
LEDs
A semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it;
the current excites the electrons, which then release photons as they return to their resting states
Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
GPS
1. Multiple satellites carrying atomic clocks are carefully synchronized with clocks on earth; these satellites emit radio signals (with constant wavespeeds)
2. GPS receivers monitor the position of these satellites and turn the timestamps from multiple (≥4) satellites into usable data as to how far away they are (and thus, where exactly the user is in relation to those satellites).

Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
Describe the basic layout of a simple combustion engine.

Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
Describe the internal mechanism of optical cameras.

Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
Colorblind glasses
Rare earth metals are infused in the lenses to absorb the specific wavelengths where red and green overlap the most (thus more clearly differentiating red from green)

How is the following process performed?
Carbon dating
1. The radioisotope 14C is constantly being created in the atmosphere
2. 14CO2 is taken up by plants (and animals who eat the plants)
3. This stops the movement of that 14C (which begins to decay)
4. The ratio of remaining 14C to 12C present in a sample will indicate its age
Carbon dating
- The radioisotope _____ is constantly being created in the atmosphere
- _____ is taken up by plants (and animals who eat the plants)
- This stops the movement of that _____ (which begins to decay)
- The _____ of _____ to _____ present in a sample will indicate its age
Carbon dating
- The radioisotope <strong>14</strong>C is constantly being created in the atmosphere
- <strong>14</strong>CO2 is taken up by plants (and animals who eat the plants)
- This stops the movement of that 14C (which begins to decay)
- The ratio of remaining 14C to 12C present in a sample will indicate its age
How does the following work and/or what is its function?
Refrigeration
- A compressor increases the temperature/pressure on a refrigerant gas
- The hot gas flows through the external condensor coils, releasing heat and condensing into a liquid
- The liquid goes through an expansion valve, reverting to a gas (temperature/pressure go way down)
- The cold gas flows through the internal evaporator coils, absorbing heat

If carbon dating is only accurate to 50,000 years ago, how do we date the past?
With other dating forms (e.g., uranium-uranium dating, uranium-lead dating, argon-argon dating, potassium-argon dating, etc.) that go back much further and happen to overlap with carbon dating
Refrigeration
- A __________ ___creases the temperature/pressure on a refrigerant gas
- The hot gas flows through the external ___________ coils, releasing heat and condensing into a liquid
- The liquid goes through an __________ valve, reverting to a gas (temperature/pressure go way down)
- The ______ gas flows through the internal ___________ coils, absorbing heat
Refrigeration

- A compressor increases the temperature/pressure on a refrigerant gas
- The hot gas flows through the external condensor coils, releasing heat and condensing into a liquid
- The liquid goes through an expansion valve, reverting to a gas (temperature/pressure go way down)
- The cold gas flows through the internal evaporator coils, absorbing heat
Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
Computer memory is made of memory cells of eight binary ______ that altogether make up one ______.
Computer memory is made of memory cells of eight binary bits that altogether make up one byte.
Describe the mechanism, function, and/or use of the following:
How many bits make up one computer memory cell (i.e. how many bits make up one byte)?
How many bytes are needed per character?
8 bits per byte;
1 byte per character
Via what two methods can a computer ‘write’ bits into either ‘0’s or ‘1’s within memory bytes?
- Semiconductor voltage changes (high or low voltages)
- Magnetization

Which part(s) of a computer memory cell (one byte, representing one character) are binary (i.e. either ‘on’ or ‘off;’ or ‘0’ or ‘1’)?
The bits
(all 8 of them can be either on or off – 28 – so 256 different characters possible)
How does any specific software system ‘know’ which patterns of 8 bits (each of which is either ‘0’ or ‘1’) corresponds to which characters?
(E.g how would a computer know that 00000001 is ‘A’ and 00000002 is ‘B?’)
Coding schemes
(preprogramed into the operating system - basically decoder charts)

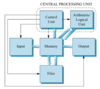
What are the four main portions of a computer (excluding input and output)?
Control unit (part of CPU)
Arithmetic/logic unit (part of CPU)
Working memory
Long-term memory