TISSUE REPAIR Flashcards
(38 cards)
Identify this pathologic repair process
accumulation of excessive amounts of collagen
remain within the confines of the original wound.
May regress spontaneously
Bundles of collagen fibers lie in a parallel arrangement
Hypertrophic scar

Identify this pathologic repair process
scar tissue grows beyond the boundaries of the original wound
Does not regress
Bundles of collagen fibers lie in a disorganized fashion
Frequently recurs after excision

Keloid
List 2 examples of stable tissues
parenchyma of liver, kidney, and pancreas
endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and smooth muscle cells
Which type of tissues/cells best fits the description given below?
can readily regenerate after injury as long as the pool of stem cells is preserved
Labile (continuously dividing) tissues
Special stain to demonstrate collagen
Masson’s Trichrome stain
See attached image. What is the underlying basis?

Exaggerated wound contraction
2 major mechanisms of liver regeneration
- Proliferation of residual hepatocytes
- Repopulation from progenitor cells
Name the localized tumor resulting from proliferation of fibroblasts, with very low metastatic potential
Desmoids (aggressive fibromatoses)
List 1 word that best fits the description given below:
Fibrosis that develops in a tissue space occupied by an inflammatory exudate
Organization
Which type of tissues/cells best fits the description given below?
Inability to proliferate in response to injury; terminally differentiated
Permanent tissues
Which type of tissues/cells best fits the description given below?
minimal proliferative activity in their normal state but capable of dividing in response to injury or loss of tissue mass
Stable tissues
List 3 examples of permanent tissues
- Neurons
- Cardiac myocytes
- Skeletal muscle cells
See the attached image and identify the abnormal pathologic repair process
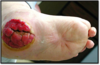
Exuberant granulation (proud flesh)
Two mechanisms via which repair occurs
- Regeneration
- Scar (connective tissue deposition) formation
List 3 examples of labile tissues
Bone marrow
Skin
GI tract
3 key differences between hypertrophic scars and keloids

Identify the pathologic repair process shown in the attached image
Etiologic basis ?

Wound dehiscence
Secondary to mechanical stress - Vomiting, coughing, or ileus
Most important mediator of fibrosis
TGF-beta
List 6 key differences between healing by first and second intention
See attached table

By when does wound strength reaches approximately 70% to 80% of normal?
Month 3
By when does the wound acquire tensile strength approximately 10% of that of unwounded skin?
End of week 1
Identify the timeline during which the following events are likely to occur in wound healing
increasing collagen deposition, regression of vessels, edema and leukocytic infiltrate
Week 2
Identify the timeline during which the following event is likely to occur in wound healing
granulation tissue formation is at its peak
Day 5
List 1 example of healing by first intention
healing of a clean, uninfected surgical incision approximated by surgical sutures




