types of mutations- genetics 2 Flashcards
(37 cards)
what are the different types of genetic mutations
Single-gene (monogenic) -Mitochondrial disorder -Chromosomal imbalance -Polygenic -Multifactorial (part genetic, part environmental
Describe the different components of DNA and which parts are spliced together
- basic architecture: - ACTG bases pared together - one strange going in the 5’->3’ direction - the other strand doing in the 3’->5’ direction genetic makeup; - promotor sequence - followed by start codon - followed by introns and exons - then terminated by a stop codon exons are spliced together the spliced together exons are transcribed and then translated
what happens in a missense mutation?
replacement of one amino acid with another
what happens in a nonsense mutation?
premature stop codon
what happens in a frameshift mutation?
caused by a deletion or insertion in a DNA sequence that shifts the way the sequence is read
what happens in a dynamic mutation?
e.g. trinucleotide repeat expansions
what are 2 examples of autosomal recessive disorders?
Cystic fibrosis PKU
what is the most common cystic fibrosis mutation?
- CFTR on chromosome 7 - regulates passage of Cl- across membranes. - Mucus becomes thickened= symptoms - Delta F 508- class 2 mutation - phenylalanine is swapped for glycine
which mutation causes PKU?
Caused by mutations in phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) exon 7 chromosome 12
How many different classes of mutation are there for cystic fibrosis- which is the most severe?
6 1 is most severe 6 is least severe
what is genetic imprinting?
mammalian epigenetic process that distinguishes maternal and paternal alleles to ensure parent-specific (monoallelic) expression of imprinted genes
Which parent allele is responsible for the expression of insulin like growth factor?
fathers
What is the parent conflict hypothesis?
Conflict of interest - mother wants baby to be small easy to birth - dad wants baby to be big and strong to show of to friends
What is the mechanism for genomic imprinting?
Closed down genes are modified using methylation this is controlled by the imprinting center which is located nearby imprinted areas on the same chromosome
Which chromosome is involved in Angelman and prader willi syndrome?
15
what happens in prayer willi syndrome?
- there is a mutation on chromosome 15 for the gene that is usually paternally expressed - although maternal chromosome 15 will carry an intact gene it will not be expressed due to genome imprinting - so only the mutated/ deleted gene on the fathers chromosome will be expressed

what is the phenotype for prader willi synrome?
mental retardation
Hypotonia
gross obesity (diabetes)
male hypogenitalism

what happens in angelmans syndrome?
Deletion in 15q11-13 region
This is the main cause
Although the paternal chr 15 contains intact copies of the 15q11-13 region, they are not expressed due to genomic imprinting

what is the phenotype of angelmans syndrome?
Mental retardation
Lack of speech
Growth retardation
Hyperactivity
Inappropriate laughter
what is an example of a denovo mutation?
- Achondroplasia
- (fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) mutation
- which causes an abnormality of cartilage formation)
7/8 of all cases caused by new mutations.
what is an example of a genetic disease that has reduced penetrance?
this type of inheritance pattern can be observed in retinoblastoma
10% of retinoblastoma population are obligate carriers. Disorder therefore has 90% penetrance
define obligate carrier
An obligate carrier is an individual who may be clinically unaffected but who must carry a gene mutation based on analysis of the family history;
what is penetrance?
Penetrance in genetics is the proportion of individuals carrying a particular variant of a gene that also express an associated trait
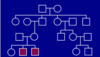
what does this pedigree show?

- an obligate carrier