VTE Prophylaxis Flashcards
(57 cards)
Prophylaxis goal?
Identify patient risk Determine risk level Select the correct regimen pharm and non pharm
Non pharm treatment Therapy for VTE
Graduated compression stockings (GCS) - good for low or moderate risk Can wear leg too big - IPC- intermittent pneumatic compression increase circulation
Pharmacologic Prophylaxis
Duration is unclear but once patient can ambulate or other RFs are gone then dc therapy - Knee replacement, treatment for 12 days after - Hip replacement 35 days after
Standard dosing for LMWH ?
Regardless of weight
Risk Level
- What are the goals for VTE treatment?
- Prevent short term complications within 6 months
- Prevent extension of clot
- Prevent embolism clot
- Prevent death
- Prevent extension of clot
- Prevent long term complications past 6 months
- Post thrombotic syndrome
- Pulmonary HTN
- Recurrent VTE
UFH is from?
Does what to clots?
From procine stomach or bovine lung
Does not dissove clot but prevents growth
Binds to AT
neutralizes Thrombin factors Xa IX, Xia, XIIa
UFH is administered?
Non specific binding site so?
IV and Sub Q
Sub Q onset is 1-2 hours
Poor bioavailability
It is critical to achieve ___ of UFH within the first?
What type of dosing is there?
therapeutic dose within 24 hours
Weight base
Standard dose
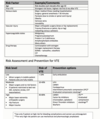
VTE chart
UFH requires close monitoring and is done by the lab test?
Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
Normal therapeutic range for aPTT?
___ to ___ the control aPTT value
28-42 seconds
1.5 to 2.5
Baseline aPTT is done?
6 hours after starting UFH infusion and 6 hours have dose change
Takes 6 hours to reach steady state
Adverse effects of UFH/
- Bleeding
- Thrombocytopenia
- HIT in 5%
- Long term use can casue Alopecia, Hyperkalemia, Osteoporosis
HIT
- Is an immune system clotting disorder
- Formation of abnormal antibodies cause platelet activation
- Monitor platelets every 2-3 days during UFH therapy
- If platelets fall below 50% from baseline or below 120000 think HIT
UFH antidote?
Protamine
UFH is ok to using in ___ patients
if patient is ____
Contraindication?
Pregnant
Can breastfeed
Contraindication is Hx of HIT
LMWH
Binds to Xa not much to do with thrombin
Advantages of LMWH?
- The anticoagulant response is more predictable less binding to plasma and cellular proteins
- Reduced need for monitoring
- Improved SUB Q bioavailability
- Longer half life
- Lower chance of HIT
- Lower chance of osteoporosis
LMWH products
Parin, Parin, Parain
Dalteparin
Enoxaparin
Tinzaparain
LMWH has much greater effect on ___
but a draw back is that there is no?
Xa activity
has no antidote
Priot to therapy of LMWH you should?
Dosing is strictly ____ based
Given ___ in ___
Baseline PT/INR, aPTT, CBC w/ platelet, serum creatinine
Weight based
QD or BID
Given Sub Q in the abdomen
AE of LMWH?
Contraindications?
- Bleeding
- Bruising
- HIT lower risk though
- Contraindicated if Hx of HIT or suspected HIT
Protamine can be used as an antidote for LMWH but it only neutralizes it by?
60%
LMWH is a great choice over UFH in patients that are?
pregnant




