W10 Carbonyl reactions Flashcards
(11 cards)
Reduction of carboxylic acid or ester
Attack of C by hydride
forms aldehyde, also forms alcohol (under acidic conditions or water)
nucleophilic substitution
requires LiAlH4 (strong enough to reduce carboxylic acids)

Reduction of aldehyde/ketone
Nucleophilic addition
Attack of C in carbonyl by hydride
Produces an alkoxide
In acidic conditions: then produces 1(aldehyde) or 2(ketone) alcohol

Aldehyde/ketone + water
Nucleophilic addition
O in water attacks carbon atom
Forms an intermediate in acid base equilibrium with a hydrate

Aldehyde/ketone reacting with alcohol
Nucleophilic addition
Acidic conditions
Aldehyde -> hemiacetal of an aldehyde -> acetal of an aldehyde
Ketone -> hemiacetal of a ketone -> acetal of a ketone

Describe mechanism for nucleophilic substitution of carbonyl groups
Called addition-elimination reactions
- Step 1: addition of nucleophile
- Step 2: elimination of leaving group -> new compound with C=O

Oxidising agents
- Different oxidising agents have different strengths
- CrO3 = gentler = isolate aldehyde under gentle conditions
- MnO4- = powerful = immediately oxidises primary alcohol to the carboxylic acid
- Jones reagent: CrO3/H2SO4 is a particularly reliable oxidant

Reducing agents
Lithium aluminium hydride LiAlH4
STRONG -> can reduce carboxylic acids to alcohols
Sodium borohydride NaBH4
WEAK -> can’t reduce carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acid reaction with thionyl chloride
Nucleophilic substitution
Forms an acid chloride
Hydroxyl is leaving group

Acid chloride reacting with alcohol
Nucleophilic substitution
chloride leaves
Forms an ester
Note: lazy notation is shown for reaction -> 1) nucleophile attack 2) leaving group

acid chlorides reacting with primary or secondary amines
Nucleophilic substitution
Forms a primary or secondary amide
H+ and Cl- are lost (forms HCl molecule)
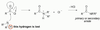
reactions of anhydrides
- Similar reactivity to acid chloride
- Can react with alcohols to produce esters
- Can react with amines to produce amides
- Note: one equivalent of carboxylic acid is released



