W3 Kinetics Flashcards
(12 cards)
3 types of rate law
1. Rate of consumption/formation of specific reactant/product
A -> 2B
B is formed at twice the rate A is consumed
Rate of reaction of B: d[B]/dt
2. Differential rate law
Rate of reaction in terms of concentration = rate of formation/consumption divided by coeffient
Has same value no matter which product/reacted is used to calculate it
Rate of reaction: d[A]/dt = 0.5*(d[B]/dt)
3. Integrated rate law
Integrate the differential law on both sides to get concentration in terms of time. What you get depends on the reaction kinetics.
Zero order reaction: rate law, integrated rate law
rate = k
Integrated rate law:
[A] = -kt + [A]0
First order reaction: rate law, integrated rate law
rate = k[A]
Integrated rate law:
ln[A] = –kt + ln[A]0
Second order reaction: rate law, integrated rate law
rate = k[A]2
Integrated rate law:
1/[A] = kt + 1/[A]0
Half life of zero order reaction
[A]0/2k
Half life of 1st order reaction
ln2/k
Half life of 2nd order reaction
1/k[A]0
Arrhenius equation
k = rate constant
A = frequency factor
Ea = activation energy
R = gas constant
T = Kelvin temperature

Arrhenius equation in graphable form
ln (natural log) to both sides
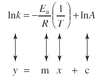
Finding activation energy if 2 rate constants (at 2 temps) are given

Steady state approximation
Assume that the concentration of any intermediates is constant - this usually only applies if concentration of intermediates is small
Sub this into the rate determining step to remove the intermediate from overall rate equation
Michaelis-Menton equation



