Week 8: Endocrine Pathology Flashcards
(127 cards)
Features of endocrine glands
- Lack ducts
- Secrete biologically active products into the blood
- Deliver hormones to target cells via receptors throughout the body
- Feedback mechanism to control hormone secretion
Features of exocrine glands
- Have ducts
- maintain contact with body surface through a duct
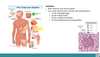
List of Endocrine organs
8 listed
- pituitary gland
- Thyroid
- Parathyroid
- Adrenal gland
- Pancreas
- Ovaries
- Testicles
- pineal gland
Pituitary gland parts
- Adenohypohysis (anterior part)
- Neurohypohysis (posterior part)
Anterior pituitary secretes
6 listed
- ACTH
- GH
- FSH
- LH
- TSH
- Prolactin

Posterior pituitary secretes
2 listed
- Oxytocin
- ADH

Adenohyphohysis
anterior pituitary
Neurohyphohysis
Posterior pituitary
Parts of the neurohyphohysis
Pars Nervosa
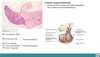
Adenohyphohysis parts
3 listed
- Pars Tuberalis
- Pars Intermediate
- Pars Tuberalis

Anterior pituitary cell types
- Acidophil cells
- Basophils
- Chromophobes
- capillaries

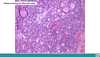
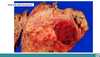
Pituitary adenomas are composed of?
neoplastic pituitary cells
Pituitary adenomas characteristics

WHO classifications of Pituitary Adenomas

Prolactin secreting adenomas symptoms
- Hyperprolactinemia
- lactation
GH secreting adenomas symptoms
- Acromegaly
- Gigantism
ACTH secreting adenomas symptoms
Cushing’s Disease
TSH secreting adenomas symptoms
Secondary thyrotoxicosis
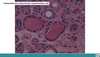
Normal vs pituitary adenoma

Normal pituitary vs pituitary adenoma histology and the reticulin stain
reticulin is fragmented

Pituitary adenoma and serological staining

Thyroid gland congenital absence
irreversible neurological damage in the infant (cretinism)
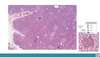
Thyroid gland characterisitcs
The thyroid gland is composed of?
Millions of rounded epithelial thyroid follicles of variable diameter