White Blood Cells Flashcards
(39 cards)
What are granulocytes
Neutrophils Basophils Eosinophils All contain granules
What are some myeloid growth factors
Granulocyte colony stimulating factor Macrophage colony stimulating factor Granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor
Granulocyte maturation

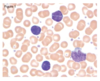
Facts about the neutrophil
Nucleus is segmented
Survives 7-10 hr in blood
It phagocytoses
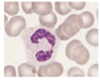
What is chemotaxis
Migration to tissues
Adhere to vessel lumen
How do neutrophils phagocytose
Superoxide dependent
Oxygen independent - antimicrobial enzymes released
Facts about eosinophil
Defence against parasitic infection
Less time in circualtion
Phagocytosis
Facts about basophil
Granules that contain histamine and heparin
Involved in a variety of immune and inflammatory reponse
Modulates inflammatory responses by releasing heparin and proteases
Facts about monocytes
Spend several days in circulation
Phagocytosis
Antigen presentation
Travel to the tissue where they develop into macrophages/histiocytes
Facts about macrophages
Phagocytic and scavenging function
Store and release iron
Photo of B lymphocytes
Also known as plasma cell
Nucleus towards edge of cell

What are NK cells
Can kill tumour cells and virus infected cells
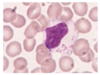
Can T and B cells be distinguished
No
How to distinguish lymphocytes
Cell markers
Immunoglobins
T cell receptors
What is the definition of leukcytosis
Too many white blood cells
What is the definition of leukopenia
Reduction in the total number of white cells
Facts about neutrophilia
Causes: infection, inflammation and tissue damage, myeloproliferative disorder (chronic myeloid leukemia)
Pregnancy
Exercise
Corticosteroids
Maybe be accompanied by toxic changes (toxic granulation)
May be more precursors in the blood film - left shift (due to increased neutrophil production)
What happens when someone has chronic myeloid leukaemia
Increase in all granulocytes
Translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22
Abnormally short chromosome 22
What is the genetic background of CML
ABL1 gene normally codes for tyrosine kinase
BCR-ABL1 encodes for a protein with unctrolled tyrosine kinase activity
What are the symptoms of CML
Enlarged spleen
How can we cure CML
Have specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Facts of neutropenia
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy (surpress activity of bone marrow)
Autoimmune diseases
Bacterial infections
Viral infections
Drugs - antipsychotic, anticonvulsant, antimalarials
Ethnic background
At risk of series infection
What is neutrophil hypersegmentation
Normally 3 to 5 lobes
Increase in neutrophil lobes - right shift
Normally due to lack of vitamin B12 or folic acid

Facts about eosinophilia
Due to allergy or parasitic infection
-asthma, eczema, drugs
Blood film show strongyloidasis