Lower Limb Nerve Injuries Flashcards
Organisation of Lower Limb nerves
- Lower limb nerves starts in anterior horn cell within spinal cord (spinal cord stops between … and L2)
- Below - cauda … - lumbar puncture go below end of spinal cord (lie laterally, iliac crest - 1 or 2 spaces above would be L3/L4 - below spinal cord end)
- Lower limb nerves starts in anterior horn cell within spinal cord (spinal cord stops between L1 and L2)
- Below - cauda equina - lumbar puncture go below end of spinal cord (lie laterally, iliac crest - 1 or 2 spaces above would be L3/L4 - below spinal cord end)
Organisation of Lower Limb nerves
- Lower limb nerves starts in anterior horn cell within spinal cord (spinal cord stops between L1 and …)
- Below - … equina - lumbar puncture go below end of spinal cord (lie laterally, iliac crest - 1 or 2 spaces above would be L…/L4 - below spinal cord end)
- Lower limb nerves starts in anterior horn cell within spinal cord (spinal cord stops between L1 and L2)
- Below - cauda equina - lumbar puncture go below end of spinal cord (lie laterally, iliac crest - 1 or 2 spaces above would be L3/L4 - below spinal cord end)
Organisation of Lower Limb nerves
- Lower limb nerves starts in … horn cell within spinal cord (spinal cord stops between L1 and L2)
- Below - cauda equina - … puncture go below end of spinal cord (lie laterally, iliac crest - 1 or 2 spaces above would be L3/L4 - below spinal cord end)
- Lower limb nerves starts in anterior horn cell within spinal cord (spinal cord stops between L1 and L2)
- Below - cauda equina - lumbar puncture go below end of spinal cord (lie laterally, iliac crest - 1 or 2 spaces above would be L3/L4 - below spinal cord end)

Organisation of Lower Limb nerves
- Lower limb nerves starts in anterior horn cell within spinal cord (spinal cord stops between L1 and L2)
- Below - cauda equina - lumbar puncture go below end of spinal cord (lie laterally, … crest - 1 or 2 spaces above would be L3/L4 - below spinal cord end)
- Lower limb nerves starts in anterior horn cell within spinal cord (spinal cord stops between L1 and L2)
- Below - cauda equina - lumbar puncture go below end of spinal cord (lie laterally, iliac crest - 1 or 2 spaces above would be L3/L4 - below spinal cord end)

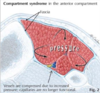
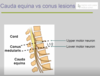
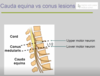
Cauda equina vs conus lesions


Landmarks for lumbar puncture
- Below end of … … - lie laterally, find iliac … - 1 or 2 spaces above = below spinal cord which will be around L3,L4 (spinal cord ends at …)
- Below end of spinal cord - lie laterally, find iliac crest - 1 or 2 spaces above = below spinal cord which will be around L3,L4 (spinal cord ends at L1/L2)
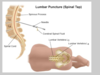
Cauda equina vs conus medullaris


Cauda equina vs conus medullaris


Cauda equina vs conus medullaris


Causes of Cauda equina
- Disc …
- … fracture
- T…
- Disc herniation
- Spinal fracture
- Tumours
3 causes of cauda equina are…
- Disc herniation
- Spinal fracture
- Tumours
Causes of Conus medullaris
- Disc …, T..
- … conditions (e.g. Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculopathy ,Sarcoidosis)
- … (E.g. CMV, HSV, EBV, Lyme, TB)
- Disc herniation, tumour,
- Inflammatory conditions (e.g. Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculopathy ,Sarcoidosis)
- Infection (E.g. CMV, HSV, EBV, Lyme, TB)
Causes of Conus medullaris (4)
- Disc herniation
- Tumour
- Inflammatory conditions (Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculopathy Sarcoidosis)
- Infection (e.g. CMV, HSV, EBV, Lyme, TB)
This shows a …
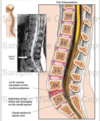
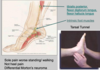
L5/S1 disc herniation compressing cauda equina
Nerve Root Entrapment – ‘sciatica
- Compression- Disc- posterior central, lateral Bone- osteophyte Ligaments
- Small canal- stenosis
- Sciatica – usually L…, S… n. root impingement
- L… n. root – exits between L…/ S…vertebral bodies S… n. root exits between S… / S… vertebral bodies
- Pain may be felt in dermatome (sharp/ superficial) or myotome (deep ache)
- Compression- Disc- posterior central, lateral Bone- osteophyte Ligaments
- Small canal- stenosis
- Sciatica – usually L5, S1 n. root impingement
- L5 n. root – exits between L5/ S1 vertebral bodies S1 n. root exits between S1 / S2 vertebral bodies
- Pain may be felt in dermatome (sharp/ superficial) or myotome (deep ache)

Nerve Root Entrapment – ‘sciatica
- Compression- Disc- posterior central, lateral Bone- osteophyte Ligaments
- Small canal- stenosis
- Sciatica – usually L5, S1 n. root …
- L5 n. root – exits between L5/ S1 vertebral bodies S1 n. root exits between S1 / S2 vertebral bodies
- Pain may be felt in … (sharp/ superficial) or … (deep ache)
- Compression- Disc- posterior central, lateral Bone- osteophyte Ligaments
- Small canal- stenosis
- Sciatica – usually L5, S1 n. root impingement
- L5 n. root – exits between L5/ S1 vertebral bodies S1 n. root exits between S1 / S2 vertebral bodies
- Pain may be felt in dermatome (sharp/ superficial) or myotome (deep ache)

Nerve Root Entrapment – ‘sciatica
- Compression- …- posterior central, lateral Bone- osteophyte Ligaments
- Small canal- stenosis
- Sciatica – usually L5, S1 n. … impingement
- L5 n. root – exits between L5/ S1 vertebral bodies S1 n. root exits between S1 / S2 vertebral bodies
- Pain may be felt in dermatome (s…/ s…) or myotome (… ache)
- Compression- Disc- posterior central, lateral Bone- osteophyte Ligaments
- Small canal- stenosis
- Sciatica – usually L5, S1 n. root impingement
- L5 n. root – exits between L5/ S1 vertebral bodies S1 n. root exits between S1 / S2 vertebral bodies
- Pain may be felt in dermatome (sharp/ superficial) or myotome (deep ache)

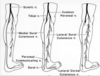
Lower Limb Root Lesions - reflex and sensory loss
- Lower limb dermatomes more variable than upper limb
- L1 … area
- L2 front of … (front pocket)
- L3 front of …
- L4 front- inner/ medial leg
- L5 outer leg, dorsum of foot, inner sole
- S1 little toe, rest of sole, back of leg
- S2 thigh to top of buttock (back pocket)
- S3-S5 concentric rings round anus/ genitalia
- Knee jerk L4, Ankle jerk S1
- Lower limb dermatomes more variable than upper limb
- L1 inguinal area
- L2 front of thigh (front pocket)
- L3 front of knee
- L4 front- inner/ medial leg
- L5 outer leg, dorsum of foot, inner sole
- S1 little toe, rest of sole, back of leg
- S2 thigh to top of buttock (back pocket)
- S3-S5 concentric rings round anus/ genitalia
- Knee jerk L4, Ankle jerk S1
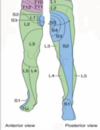
Lower Limb Root Lesions - reflex and sensory loss
- Lower limb dermatomes more variable than upper limb
- L1 inguinal area
- L2 front of thigh (front pocket)
- L3 front of knee
- L4 front- inner/ … leg
- L5 … leg, … of foot, inner …
- S1 … toe, rest of …, back of leg
- S2 thigh to top of … (back pocket)
- S3-S5 concentric rings round anus/ genitalia
- Knee jerk L4, Ankle jerk S1
- Lower limb dermatomes more variable than upper limb
- L1 inguinal area
- L2 front of thigh (front pocket)
- L3 front of knee
- L4 front- inner/ medial leg
- L5 outer leg, dorsum of foot, inner sole
- S1 little toe, rest of sole, back of leg
- S2 thigh to top of buttock (back pocket)
- S3-S5 concentric rings round anus/ genitalia
- Knee jerk L4, Ankle jerk S1
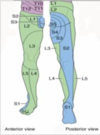
Lower Limb Root Lesions - reflex and sensory loss
- Lower limb dermatomes more variable than upper limb
- L1 … area
- L2 front of thigh (… pocket)
- L3 front of knee
- L4 front- inner/ medial leg
- L5 outer leg, dorsum of foot, inner sole
- S1 little toe, rest of sole, back of leg
- S2 … to top of buttock (… pocket)
- S3-S5 … rings round anus/ genitalia
- Knee jerk L4, Ankle jerk S1
- Lower limb dermatomes more variable than upper limb
- L1 inguinal area
- L2 front of thigh (front pocket)
- L3 front of knee
- L4 front- inner/ medial leg
- L5 outer leg, dorsum of foot, inner sole
- S1 little toe, rest of sole, back of leg
- S2 thigh to top of buttock (back pocket)
- S3-S5 concentric rings round anus/ genitalia
- Knee jerk L4, Ankle jerk S1

Lower Limb Root Lesions - reflex and sensory loss
- Lower limb dermatomes more variable than upper limb
- L1 inguinal area
- L2 front of thigh (front pocket)
- L3 front of …
- L4 front- inner/ medial leg
- L5 outer leg, dorsum of foot, inner sole
- S1 little toe, rest of sole, back of leg
- S2 thigh to top of buttock (back pocket)
- S3-S5 concentric rings round …/ …
- … jerk L4, … jerk S1
- Lower limb dermatomes more variable than upper limb
- L1 inguinal area
- L2 front of thigh (front pocket)
- L3 front of knee
- L4 front- inner/ medial leg
- L5 outer leg, dorsum of foot, inner sole
- S1 little toe, rest of sole, back of leg
- S2 thigh to top of buttock (back pocket)
- S3-S5 concentric rings round anus/ genitalia
- Knee jerk L4, Ankle jerk S1

Lower Limb Root Lesions - weakness
- L1/2 … flexion
- L3/4 … extension
- L4 … inversion
- L5 Knee flexion Ankle …
- Toe extension
- Foot inversion and eversion
- S1 Knee flexion
- Ankle plantar flexion
- Toe flexion Foot eversion
- L1/2 Hip flexion
- L3/4 Knee extension
- L4 Foot inversion
- L5 Knee flexion Ankle dorsiflexion
- Toe extension
- Foot inversion and eversion
- S1 Knee flexion
- Ankle plantar flexion
- Toe flexion Foot eversion
Lower Limb Root Lesions - weakness
- L1/2 Hip flexion
- L3/4 Knee extension
- L4 Foot inversion
- L5 … flexion … dorsiflexion
- … extension
- Foot … and …
- S1 Knee flexion
- Ankle plantar flexion
- Toe flexion Foot eversion
- L1/2 Hip flexion
- L3/4 Knee extension
- L4 Foot inversion
-
L5 Knee flexion Ankle dorsiflexion
- Toe extension
- Foot inversion and eversion
- S1 Knee flexion
- Ankle plantar flexion
- Toe flexion Foot eversion
Lower Limb Root Lesions - weakness
- L1/2 Hip flexion
- L3/4 Knee extension
- L4 Foot inversion
- L5 Knee flexion Ankle dorsiflexion
- Toe extension
- Foot inversion and eversion
- S1 … flexion
- Ankle … flexion
- Toe … Foot …
- L1/2 Hip flexion
- L3/4 Knee extension
- L4 Foot inversion
- L5 Knee flexion Ankle dorsiflexion
- Toe extension
- Foot inversion and eversion
-
S1 Knee flexion
- Ankle plantar flexion
- Toe flexion Foot eversion
Lower Limb Root Lesions - weakness
- …/… Hip flexion
- …/… Knee extension
- … Foot inversion
- … Knee flexion Ankle dorsiflexion
- Toe extension
- Foot inversion and eversion
- … Knee flexion
- Ankle plantar flexion
- Toe flexion Foot eversion
- L1/2 Hip flexion
- L3/4 Knee extension
- L4 Foot inversion
-
L5 Knee flexion Ankle dorsiflexion
- Toe extension
- Foot inversion and eversion
-
S1 Knee flexion
- Ankle plantar flexion
- Toe flexion Foot eversion
Lower Limb Root Lesions - weakness
- L1/2 Hip flexion
- L3/4 Knee …
- L4 Foot …
- L5 Knee … Ankle dorsiflexion
- Toe …
- Foot inversion and …
- S1 Knee …
- Ankle plantar flexion
- Toe flexion Foot eversion
- L1/2 Hip flexion
- L3/4 Knee extension
- L4 Foot inversion
- L5 Knee flexion Ankle dorsiflexion
- Toe extension
- Foot inversion and eversion
- S1 Knee flexion
- Ankle plantar flexion
- Toe flexion Foot eversion
Lower Limb Root Lesions - weakness
- L1/2 … flexion
- L3/4 … extension
- L4 Foot inversion
- L5 Knee flexion … dorsiflexion
- Toe extension
- … inversion and eversion
- S1 Knee flexion
- … plantar flexion
- Toe flexion … eversion
- L1/2 Hip flexion
- L3/4 Knee extension
- L4 Foot inversion
- L5 Knee flexion Ankle dorsiflexion
- Toe extension
- Foot inversion and eversion
- S1 Knee flexion
- Ankle plantar flexion
- Toe flexion Foot eversion
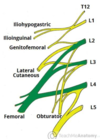
Lumbar plexus

Sacral plexus

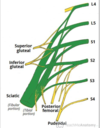
Lumbosacral Plexus Lesions
- … (large head, prolonged labour)- esp … n., numbness inner thigh, pudendal n.
- Structural
- … (on Warfarin)
- Abscess
- … – infiltration
- Trauma
- Non structural
- Inflammatory
- Diabetes
- Vasculitis
- Radiotherapy
- Childbirth (large head, prolonged labour)- esp obturator n., numbness inner thigh, pudendal n.
- Structural
- Haematoma (on Warfarin)
- Abscess
- Malignancy – infiltration
- Trauma
- Non structural
- Inflammatory
- Diabetes
- Vasculitis
- Radiotherapy
Lumbosacral Plexus Lesions
- Childbirth (large .., prolonged ..)- esp obturator n., numbness inner thigh, pudendal n.
- Structural
- Haematoma (on Warfarin)
- A…
- Malignancy – infiltration
- Trauma
- Non structural
- I…
- D…
- Vasculitis
- Radiotherapy
- Childbirth (large head, prolonged labour)- esp obturator n., numbness inner thigh, pudendal n.
- Structural
- Haematoma (on Warfarin)
- Abscess
- Malignancy – infiltration
- Trauma
- Non structural
- Inflammatory
- Diabetes
- Vasculitis
- Radiotherapy
Lumbosacral Plexus Lesions
- Childbirth (large head, prolonged labour)- esp obturator n., … inner thigh, pudendal n.
- Structural
- Haematoma (on W…)
- Abscess
- Malignancy – infiltration
- T…
- Non structural
- Inflammatory
- Diabetes
- V…
- R..
- Childbirth (large head, prolonged labour)- esp obturator n., numbness inner thigh, pudendal n.
- Structural
- Haematoma (on Warfarin)
- Abscess
- Malignancy – infiltration
- Trauma
- Non structural
- Inflammatory
- Diabetes
- Vasculitis
- Radiotherapy
Femoral Nerve Organisation
- Hip …, Iliopsoas affected if proximal damage (above inguinal Ligament)
- Only knee … if below inguinal ligament (preserve hip flexion)
- Distal lesion may produce a pure motor or pure … syndrome
- Hip flexors, Iliopsoas affected if proximal damage (above inguinal Ligament)
- Only knee extension if below inguinal ligament (preserve hip flexion)
- Distal lesion may produce a pure motor or pure sensory syndrome

Femoral Nerve Organisation
- Hip flexors, … affected if proximal damage (above … Ligament)
- Only knee extension if below … ligament (preserve hip …)
- … lesion may produce a pure motor or pure sensory syndrome
- Hip flexors, Iliopsoas affected if proximal damage (above inguinal Ligament)
- Only knee extension if below inguinal ligament (preserve hip flexion)
- Distal lesion may produce a pure motor or pure sensory syndrome

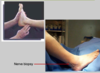
Femoral / Lateral Cutaneous Nerves
- Femoral N.
- Weakness
- Femoral nerve responsible for Hip … (iliacus)
- Femoral nerve responsible for Knee …
- Loss of Knee Jerk
- Can’t do …
- Femoral N.
- Weakness
- Femoral nerve responsible for Hip flexion (iliacus)
- Femoral nerve responsible for Knee Extension
- Loss of Knee Jerk
- Can’t do stair

Femoral / Lateral Cutaneous Nerves
- Femoral N.
- …
- Femoral nerve responsible for Hip flexion (iliacus)
- Femoral nerve responsible for Knee Extension
- Loss of Knee …
- Can’t do stair
- Femoral N.
- Weakness
- Femoral nerve responsible for Hip flexion (iliacus)
- Femoral nerve responsible for Knee Extension
- Loss of Knee Jerk
- Can’t do stair

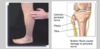
Femoral N. damage
- Femoral …
- Childbirth
- S…
- Gynae procedures, esp …, femoral a. bypass/ puncture)
- Femoral fracture
- Childbirth
- Surgery
- Gynae procedures, esp hysterectomy, femoral a. bypass/ puncture)
Femoral N. damage
- Femoral …
- C…
- Surgery
- … procedures, esp hysterectomy, femoral a. bypass/ puncture)
- Femoral fracture
- Childbirth
- Surgery
- Gynae procedures, esp hysterectomy, femoral a. bypass/ puncture)
Sciatica
- Pain in sciatic n. distrib
- Nerve root entrapment (usually L… / S…)
- Differential diagnosis: … – pain may radiate not below knee, Sacroiliac joints
- Causes:
- Trauma
- H…
- Rarely sciatic nerve compression per se (P.. synd)
- Or misplaced IM injections
- Pain in sciatic n. distrib
- Nerve root entrapment (usually L5 / S1)
- Differential diagnosis: Hip – pain may radiate not below knee, Sacroiliac joints
- Causes:
- Trauma
- Haematoma
- Rarely sciatic nerve compression per se (Piriformis synd)
- Or misplaced IM injections

Sciatica
- Pain in sciatic n. distrib
- Nerve root … (usually L5 / S1)
- Differential diagnosis: Hip – pain may radiate not below knee, Sacroiliac joints
- Causes:
- T…
- Haematoma
- Rarely sciatic nerve … per se (Piriformis synd)
- Or misplaced … injections
- Pain in sciatic n. distrib
- Nerve root entrapment (usually L5 / S1)
- Differential diagnosis: Hip – pain may radiate not below knee, Sacroiliac joints
- Causes:
- Trauma
- Haematoma
- Rarely sciatic nerve compression per se (Piriformis synd)
- Or misplaced IM injections

Sciatica
- Pain in sciatic n. distrib
- Nerve … entrapment (usually L5 / S1)
- Differential diagnosis: Hip – pain may radiate not below knee, S… joints
- Causes:
- Trauma
- Haematoma
- Rarely sciatic nerve compression per se (… synd)
- Or misplaced IM injections
- Pain in sciatic n. distrib
- Nerve root entrapment (usually L5 / S1)
- Differential diagnosis: Hip – pain may radiate not below knee, Sacroiliac joints
- Causes:
- Trauma
- Haematoma
- Rarely sciatic nerve compression per se (Piriformis synd)
- Or misplaced IM injections

Sciatica
- Pain in sciatic n. distrib
- Nerve root entrapment (usually L5 / S1)
- Differential diagnosis: Hip – pain may radiate not below …, Sacroiliac joints
- Causes:
- Trauma
- Haematoma
- … sciatic nerve compression per se (Piriformis synd)
- Or misplaced IM …
- Pain in sciatic n. distrib
- Nerve root entrapment (usually L5 / S1)
- Differential diagnosis: Hip – pain may radiate not below knee, Sacroiliac joints
- Causes:
- Trauma
- Haematoma
- Rarely sciatic nerve compression per se (Piriformis synd)
- Or misplaced IM injections

Pain from … radiates from the buttock down the leg and can travel as far as to the feet and toes
Pain from sciatica radiates from the buttock down the leg and can travel as far as to the feet and toes
? Piriformis Syndrome
- Controversial as to whether muscle … per se can cause tingling in … and down … (eg after exercise or straining, or prolonged sitting)
- Probably may rarely occur in those with anatomical predisposition.
- No consensus on criteria Diagnosis of …
- Controversial as to whether muscle compression per se can cause tingling in buttock and down leg (eg after exercise or straining, or prolonged sitting)
- Probably may rarely occur in those with anatomical predisposition.
- No consensus on criteria Diagnosis of exclusion

? Piriformis Syndrome
- Controversial as to whether muscle compression per se can cause tingling in buttock and down leg (eg after … or straining, or prolonged …)
- Probably may rarely occur in those with … predisposition.
- No consensus on criteria Diagnosis of exclusion
- Controversial as to whether muscle compression per se can cause tingling in buttock and down leg (eg after exercise or straining, or prolonged sitting)
- Probably may rarely occur in those with anatomical predisposition.
- No consensus on criteria Diagnosis of exclusion

Sciatic N. Injury
- Apart from: Hip … Knee … Hip … (femoral nerve first 2 and obturator …)
- Sciatic nerve or its branches, are motor to virtually all other muscle groups in the leg
- Isolated Hip … – sciatic n. Pelvic/ sacral fracture – sacral plexus)
- Apart from: Hip flexion Knee extension Hip adduction (femoral nerve first 2 and obturator adduction)
- Sciatic nerve or its branches, are motor to virtually all other muscle groups in the leg
- Isolated Hip fracture – sciatic n. Pelvic/ sacral fracture – sacral plexus)

Sciatic N. Injury
- Apart from: Hip flexion Knee extension Hip adduction ((… nerve first 2 and … adduction))
- Sciatic nerve or its branches, are motor to virtually all other muscle groups in the leg
- Isolated Hip fracture – sciatic n. Pelvic/ sacral fracture – sacral plexus)
- Apart from: Hip flexion Knee extension Hip adduction (femoral nerve first 2 and obturator adduction)
- Sciatic nerve or its branches, are motor to virtually all other muscle groups in the leg
- Isolated Hip fracture – sciatic n. Pelvic/ sacral fracture – sacral plexus)