Congenital Lesions of the Face and Neck Flashcards
1
Q
Development of the Face
- The external human face develops between the … and … week of embryonic development.
- Many opportunities for abnormal development
- Critical periods of development
A
- The external human face develops between the 4th and 6th week of embryonic development.
- Many opportunities for abnormal development
- Critical periods of development

2
Q
Development of the Face
- These developments take place in week … (left) and week … (right)

A
at 4 weeks and 5 weeks
3
Q
Development of the Face
- These developments take place in week … (left) and week … (right)

A
at 6 weeks and 7 weeks

4
Q
Development of the Face
- These developments take place in week … (left) and week … (right)

A
At 8 Weeks and 9 Weeks

5
Q
Electron Micrograph showing development of the …

A
face
6
Q
Basic Facial Structure
- 1 x f…
- 2 x …medial
- 2 x …lateral
- 2 x m….
- 2 x m…
- m… and m… 1st … arch
- m… arch
A
- 1 x frontonasal
- 2 x nasomedial
- 2 x nasolateral
- 2 x maxillary
- 2 x mandibular
- maxillary and mandibular 1st pharyngeal arch
- mandibular arch

7
Q
Formation of the Palate
- The maxillary process develops … processes
- Should fuse to form … palate in midline
- Anteriorly, … palate formed
- Part of that becomes … palate
- Any problem in formation of these and fusion of these - give rise to conditions of … …
A
- The maxillary process develops palatine processes
- Should fuse to form hard palate in midline
- Anteriorly, primary palate formed
- Part of that becomes soft palate
- Any problem in formation of these and fusion of these - give rise to conditions of cleft palate

8
Q
Electron Micrograph showing what happens during formation of the …

A
Palate
9
Q
Abnormalities in Development of Face
- A-C =
- D-E =

A
- A-C = cleft lip
- D-E = cleft palate
10
Q
The Pharyngeal Arches
- How many?
- What are they called?
- They all have m.., car…, n… and a branch of the … arch
A
- Mandibular, hyoid, third and fourth
- All have mesoderm, cartilage, a nerve, and a branch of the aortic arch

11
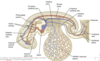
Q
The Pharyngeal Apparatus
A

12
Q
Pharyngeal Pouches - Embryology
A

13
Q
Pharyngeal Apparatus
A

14
Q
Embryology - Pharyngeal Apparatus
A
15
Q
Pharyngeal Arch 1 is the … arch
A
Pharyngeal Arch 1 is the Mandibular arch













