Amino Acids Flashcards
(24 cards)
Alanine
Ala, A, Aliphatic
A saturated hydrocarbon, important in hydrophobic interactions.

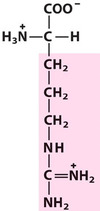
Arginine*
Arg, R, Basic
Hydrophilic
Positively charged at neutral pH.
The only amino acid with 4 Nitrogen atoms.
Asparagine
Asn, N
H-bonds

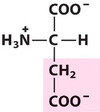
Aspartic acid
Asp, D, Acidic
Negatively-charged at physiological pH.
They have carboxyl groups. Therefore, they can:
- form hH bonds
- contribute to enzyme catalysis (e.g. Glu in lysozyme)
- form salt (ionic) bonds with opposite charge (e.g. stabilising deoxy-Hb)
Asparagine or aspartic acid*
Asx, B
Cysteine
Cys, C, Sulfur-containing
The most important thing about Cysteine is its ability to form disulphide bonds within and between polypeptides.
Disulphide bonds allow the stabilisation of exported proteins such as:
hormone (e.g. insulin) structural proteins (e.g. keratin) digestive enzymes (e.g. pepsin)

Glutamine
Gln, Q
H-bonds

Glutamic Acid
Glu, E, Acidic
Excitatory NT
Negatively-charged at physiological pH.
They have carboxyl groups. Therefore, they can:
- form H bonds
- contribute to enzyme catalysis (e.g. Glu in lysozyme)
- form salt (ionic) bonds with opposite charge (e.g. stabilising deoxy-Hb)

Glutamine or Glutamic Acid*
Glx, Z
Glycine
Gly, G, Aliphatic
In a protein, glycine allows more structural flexibility because of the side chain’s minimal steric hindrance.

Histidine
His, H, Basic
Hydrophilic
His has an imidazole ring.
It is often found in the active sites of enzymes.
There, its imidazole ring can readily switch between the uncharged state and positively-charged state, to catalyse the making and breaking of bonds.
It is required for the synthesis of histamine (by decarboxylation).
The heterocyclic imidazole ring is planar and has delocalised pi orbitals, making it aromatic. However, unlike Phe, Tyr and Trp, it is much more polar than non-polar.

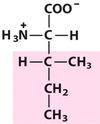
Isoleucine*
IIe, I, Aliphatic
An isomer of leucine;
Bulky side chain;
This residue and Thr have a chiral β-carbon.
Leucine
Leu, L, Aliphatic
Two words: LEUCINE ZIPPER !!
It allows two proteins to bind together via hydrophobic associations.

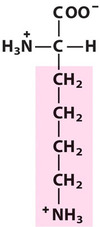
Lysine*
Lys, K, Basic
Hydrophilic
Positively charged at neutral pH. The reactive -NH3+ in Lys can form cross-linked structures such as:
Desmosine linkages in elastin;
Peptide bridges of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell walls (more about peptidoglycan in Mirobiology).
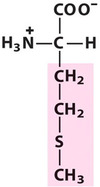
Methionine
Met, M, Sulfur-containing
An aliphatic group with a thioether;
Met is always the first amino acid to be incorporated into a protein. However, following synthesis, the N-terminus of proteins is frequently modified. So most proteins do not have Met at their N-termini.
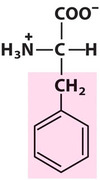
Phenylalanine
Phe, F, Aromatic
Hydrophobic in nature and neutral at any pH;
It is the most non-polar of the aromatic amino acids.
Why interesting? A genetic lack of Phe hydroxylase prevents Phe —-> Tyr. Excess Phe can cause mental retardation! (PKU)
Proline
Pro, P, Aliphatic
Not strictly an amino acid, proline is actually an imino acid, i.e. in peptides and proteins it has no free amine;
It influences protein folding by introducing kinks into the protein backbones.

Serine
Ser, S, Aliphatic Hydrox
Ser is small and polar. It is the hydroxylated version of Ala.
It is important in the active site of some enzymes e.g. Acetylcholinesterase.

Threonine
Thr, T, Aliphatic Hydrox
Like Ile, Thr has 2 centres of asymmetry, the a-carbon and the β-carbon.
It is an essential amino acid.

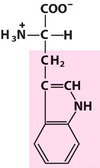
Tryptophan
Trp, W, Aromatic
Has an indole ring, joined to a methylene group;
Like Phe, it is hydrophobic in nature and neutral at any pH;
Trp is one of the essential amino acids, and is required for the synthesis of the neurotransmitter serotonin.
Tyrosine
Tyr, Y, Aromatic
Same structure as Phenylalanine, but with an extra hydroxyl group;
Therefore, it can form hydrogen bonds.
It can also be phosphorylated - this is a very important feature in the regulation of cell replication.

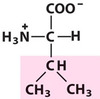
Valine
Val, V, Aliphatic
A saturated hydrocarbon, important in hydrophobic interactions.
Aliphatic
Draw a typical AA reaction to form a polypeptide



