Biochem: Ch 1 Flashcards
(114 cards)
amino acids structure
amino group (-NH2)
carboxyl group. (-COOH)
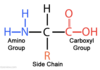
α-amino acids
amino and carboxyl group bonded to the same carbon (α-carbon)
aka proteinogenic amino acids
side chains of amino acids (R groups)
determine the properties of amino acids
all amino acids are ___ except for ___
chiral
glycine
thiol
-SH
general trend of nonpolar, nonaromatic amino acids
alkyl groups
(7)

general trend of aromatic amino acids
conjugated ring
(3)

general trend of polar amino acids
OH, amide, or thiol
(5)

general trend of negatively charged (acidic) amino acids
carboxylate/carboxylic acid
(2)

general trend of positively charged (basic) amino acids
pos charged N atom
(3)

general trend of hydrophobic amino acids
long alkyl side chains
hydrophobic amino acids are more likely to be found
in interior of proteins, away from water on surface of protein
general trend of hydrophilic amino acids
charged side chains and amides
hydrophilic amino acids are more likely to be found
surface of protein
what is the stereochemistry of chiral amino acids that appear in eukaryotic proteins?
L or D
exception?
L
no
what is the stereochemistry of chiral amino acids that appear in eukaryotic proteins?
(S) or (R)
exception?
(S)
cysteine
amino acids
ionizable groups tend to…
gain protons under acidic conditions
lose protons under basic conditions
at low pH, ionizable groups tend to be
protonated
at high pH, ionizable groups tend to be
deprotonated
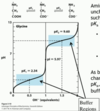
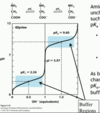
pH < pKa
majority of species will be protonated
pH > pKa
majority of species deprotonated
pKa of carboxyl group
pKa1 = carboxyl group = 2
amino acids under acidic conditions
tend to be positively charged
carboxylic acid group –> fully protonated (-COOH) - neutral
amino group –> fully protonated (-NH3+) - pos charge
pKa of amino group
pKa2 = amino group = 9-10