Kaplan Organic Chem: Chapter 1 Flashcards
(56 cards)
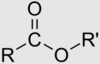
carbonyl group
carbon double bonded to an oxygen

aldehyde structure
carbonyl, R group, and H

ketone structure
carbonyl group and 2 R groups

alkanes
CnH2n+2
hydrocarbons that lack pi bonds
usually end with “ane”
methane, propane, butane
steps to nomenclature
- select parent chain –> longest chain
- for chains with equal lengths, choose the one with more substituents
- number the parent chain
- give first substituent the lower possible number
- if tie, choose chain where 2nd sub has the lower number
- name the subsituents based on where and how many
- arrange the subs alphabetically
- place the locants in front of each substituent
primary carbon
1°
depends on number of carbons directly attached

secondary carbon
2°

tertiary carbon
3°

quarternary carbon
4°
depends on number of carbons directly attached

Assessing Stability
- correct electronegativity
- size: bigger = more stable
- more resonance = more stable –> pi bond being spread
- induction: pull away from neg charged region more acidic –> sigma bonds
- orbitals: triple bond more acidic
- lone pair - 25% sp3 less stable
nomenclature
n-
“normal”
n-propyl –> straight chain alkane
nomenclature
multiple substituents of the same type
di-, tri-, tetra- etc
highlight the parent chain

longest chain must include hydroxyl group

highlight the parent chain


name substituents then name molecule

4-ethyl-2,3-dimethylheptane

hydrocarbons
compounds that only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms
alcohols
contain at least one OH group
alkyl halides
alkanes with halogen subsituents
fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, iodo-
alkene
alkanes with double bonds
alkyne
alkanes with triple bonds
alkane name
1 carbon
methane
alkane name
2 carbons
ethane
alkane name
3 carbons
propane
alkane name
4 carbons
butane