Chapter 6 Flashcards
(32 cards)
What is recombinant DNA technology?
allows DNA fragment from any source to be joined in vitro with a nucleic acid vector that can replicate autonomously in microorganisms

How do you clone and isolate DNA?
1) ligate DNA into a piece of nucleic acid (or vector) that can autonomously replicate in living organism
2) Transfer recombinant vecotrs into host cells
3) grow host cells in isolated colonies so each colony only contains one recombinant vector
4) each cultured colony is a clone; all members are genetically identical
5) select colony for study
6) grow a large quantity of that colony
7) lyse the host cells and re-isolate the replicated recombinant vectors
remove (by restriction enzyme cutting) cloned DNA from vector
How do you clone restriction fragments of DNA?
- restriction endonucleases cut DNA specifically at palindrome sequences, yielding restriction fragments of chromosomes
- restriction fragments are cloned in vectors
- cloned fragments are re-isolated from cloned recombinant vecotrs
- restriction fragments from each clone are sequenced
What are restriction endonucleases?
enzymes isolated from bacteria
recognize double stranded DNA sequenced called palindromes (inverted repeats) usually 4-8 base pairs in length
–in bacteria act as part of restriction/modification system that protect bacteria from infection by DNA viruses
ex. ECoRI

What is a palindrome
sequence that reads the same backward and forward

What is the difference between an exonuclease and an endonuclease?
exonuclease: begin at one end and release single nucleotides
endonuclease: cleave internal PDE and release restriction fragments
What are sticky ends on DNA restriction fragments?
offset cuts within palindrome
facilitating recombination of a restriction fragment with the vector DNA

What is a vector and what is it used for?
piece of DNA capable of autonomous replication in host cell
–has one type of palindrome recognized by restriction endonuclease
–origin for autonomous replication
–at least one gene for restistance to an antibiotic (allows selection for colonies with recombinant plasmids)
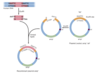
How are restriction fragments cloned using vectors?
- vector is cut with restriction endonuclease and mixed with DNA restriction fragments to be cloned
- DNA ligase is used to form permanent PDE bond between fragment and vector–>recombinant DNA
- bacteria with recombinant plasmid is resistant to one antibiotic but sensitive to another
- collection of colonies produced = genomic DNA library
What can genomic libraries be used for?
- identify protein coding genes
- identify restriction endonuclease sites
- identify other gneetic markets
- non-expressed DNA (enhancers, promoters, introns, noncoding DNA between gene regions)
What are restriction maps?
line drawings of DNA identifying sites cut by restriction endonucleases
–identify potential RFLP makers for genetic diagnosis
When is cDNA used instead of DNA restriction fragments?
–want cloned gene expressed in cell (coding sequence must be cloned intact)
–if cloned eukaryotic gene is expressed in bacteria (to make recobinant proteins) gene can’t contain introns, which can’t be processed in prokaryotic cell
How do you produce cDNA by reverse transcription of mRNA?
reverse transcriptase use in vitro to produce double stranded cDNA that is combined with vector to make recombinant dNA for cloning
RESULT:
- all genes expressed will be cloned along with desired gene
- none of the non-expressed DNA in the cell will be cloned
- each cDNA represent the complete coding sequence of a gene
cDNA have no introns
-an expression library is produced at the end of the cloning procedure

What are expression libraries used for?
- sequence specific genes and identify disease-causing mutations
- produce recombinant proteins (insulin, factor VIII, HbsAg for vaccination)
- conduct gene replacement therapy
- produce transgenic mice
What is the difference between genomic libraries and cDNA (expression) libraries?

How do you screen libraries for a specific DNA sequence?
- blot is made from plate
- colonies on the blot are lysed and treated with radioactive probe specific for DNA sequence (32P-DNA) or in expression libraries for recombinant protein (125I-antibody)
- an autoradiogram of the probed blot is produced and radioactive colony identified

What is genes cloned from cDNA used for?
- produce recombinant proteins
- carry out gene therapy on individuals with genetic diseases
- produce transgenic and knockout mice in which to study human disease producing genes
What do you need provide if you want to clone and obtain recombinant protein?
appropriate sequences required for transcription and translation in cloning host cell

What therapeutic proteins are mass-produced as recombinant proteins?
- human insulin (diabetes)
- HbsAg (vaccinations)
- Factor VIII (hemophilia)
What is gene therapy?
introduce a normal copy of a gene that is defective into tissues that give rise to pathology of genetic diseases
What is an example of gene therapy in SCID?
mutation in gamma chain common to several interleukin receptors

Waht is the difference between ex vivo and in vivo?
Ex vivo: cells modified outside the body, then transplanted back in
In vivo: genes changed in cells still in body
How do gene vectors work?
Usually modified viruses
portion of viral genome is replaced with cloned gene (as DNA or RNA) so virus can infect but not complete its replication cycle
Describe retroviruses as gene delivery vectors.
insert their RNA in form of reverse-transcribed DNA into chromosomes of dividing host cells
–requirement that host cells be replicating for successful infection
–random integration of the retroviral genome into chromosome
(poses risk of integrating near and activating a host ocnogene)







