Chapter 8 Flashcards
(37 cards)
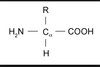
What is the general structure of an amino acid?
What are the hydrophobic amino acids?
nonpolar aliphatic side chains: Glycine (Gly), Alanine (Ala), Valine (Val), Leucine (Leu), Isoleucine (Ile), Proline (Pro)
aromatic side chains: phenylalanine (Phe), Tyrosine (Tyr), Tryptophan (Trp)

What can phenylalanine and tyrosine form?
Catecholamines
What can tryptophan form?
serotonin, niacin
What amino acids are metabolized normally in maple syrup urine disease?
valine, leucine, and isoleucine
What is the significance of proline?
secondary amine, whose presence in a protein disrupts normal secondary structure
What are the hydrophilic amino acids?
positively charged R groups: lysine (Lys), Arginine (Arg), Histidine (His)
negatively charged R groups: Aspartate (Asp), Glutamate (Glu)
polar, uncharged R groups: Serine (Ser), Threonine (Thr), Cysteine (Cys), Methionine (Met), Asparagine (Asn), Glutamine (Gln)

What do hydrophilic side chainns contain?
O or N atoms
What are the charges of acidic amino acids and basic amino acids?
acidic (aspartic and glutamic acids): carboxyl groups are negatively charged at physiologic pH
basic (lysine, arginine, histidine): nitrogen atoms are positively charged at physiologic pH
What amino acids are sites for O-linked glycosylation of proteins and where does this occur?
serine and threonine
posttranslation modification associated with the Golgi apparatus
What is the site for N-linked glycosylation of protein and where does it occur?
asparagine
posttranslational modification that is associated with the ER
What is the significance of cysteine?
contains sulfur and can form disulfide bonds, which stabilizes tertiary structure
destroying disulfide bonds denatures proteins
What is the significance of methionine?
sulfur-containing amino acid
part of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), methyl donor in biochemical pathways
What is sickle cell anemia characterized by?
severe pain in bones, abdomen, chest, and periods of hemolytic problems
vaso-occlusive pain lasting 1 week
crises precipitated by dehydration or infection
What mutation occurs in sickle cell anemia (HbS) and sickle cell anemia-like hemoglobinpathy (HbC)?
HbS: substitution of valine for glutamate at position 6 of Hb
–HbS has one less negative charges overall compared with HbA
HbC: substitution of lysine for glutamate at position 6
–HbC has two more positive charges compared with HbA
What is protein turnover?
When broken down proteins are replaced
How are proteins broken down?
lysosomal proteases digest endocytosed proteins
large cytoplasmic complexes (proteasomes) digest older or abnormal proteins that have been covalently tagged with a protein (ubiquitin) for destruction
What are the essential amino acids?
Amino acids that can’t be synthesized in humans and must be provided by dietary sources
arginine (only during periods of positive nitrogen balance, growth), histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, valine
What is nitrogen balance?
Normal condition where amount of nitrogen incorporated into the body each day = amount excreted
Waht is negative nitrogen balance?
when nitrogen loss exceeds incorporation
ex. protein malnutrition (kwashiorkor), dietary deficiency of even one essential amino acid, starvation, uncontrolled diabetes, infection
What is positive nitrogen balance?
amoung of nitrogen incorporated exceeds the amoung excreted
associated with: growht, pregnancy, recovery phase of injury or surgery, recovery from condition associated with negative nitrogen balance
What is the difference between kwashiorkor and marasmus?
marasmus: chronic deficiency of calories
kwashiorkor: edema
What is ∆G?
amount of energy required or released per mole of reactant
tells you nothing about rate of reaction
What is the rate of the reaction determined by?
energy of activation ∆G†, which is the energy required to initiate the reaction
increased by enzymes
enzymes decrease energy of activation ∆G†









