Chapter 5 Flashcards
(34 cards)
What are examples of chromatin remodeling?
1) transcription factors bind to DNA and recruit coactivators (histone acetylases)
2) HIstone acetylases (gene expression) and histone deacetylases (inactie chromatin)
3) lysyl residues in histones are acetylated–decreaseing positive charge and weakening interaction with DNA
4) chromatin remodeling engine binds to acetylated lysyl residues and reconfigures DNA to expose promoter region
5) additional transcription factors bind in promoter region and recruit RNA polymerase
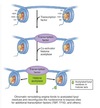
What causes basal (low level) transcription?
transcription complex with general transcription factors and RNA polymerase
How allows increased transcription?
response elements bind to to specific transcriptoin factors
–many response elements grouped to form enhancer
What is a upstream promotor?
close proximity ot -25 sequence
1) CCAAT box (around -75) binds general TF NF-1
2) GC rich sequence binds general TF SP-1
–binding sites for RNA polymerase and general transcription factors

What are enhancers?
binding sites for activator proteins
not required for transcription
1) up to 1,000 bp away from gene
2) upstream, downstream, within intron
4) act in tissue-specific manner
5) brought close to basal promoter region in space by bending of DNA molecule
binding site for specific transcriptoin factor

What is the difference between a cis and trans regulatory element?
**Cis regulator: **DNA regulatory base sequences (promoters, enhancers, response elements, UPE) that are binding sites for proteins
**Trans regulator: **transcription factors (and genes that encode them)
–can diffuse through cell to point of action
What are transcription factors?
activator proteins that bind to response elements
–have:
DNA binding domain
binds to nucleotide sequence in promoter or response element
ex. zinc fingers (steroid hormones), leucine zippesr (cAMP-dependent TF), helix-loop-helix, helix-turn-helix (homeodomain proteins encoded by homeotic/homeobox genes))
**Activation domain **
allows TF to bind to other transcription factors
interact with RNA polymerase II to stabilize initiation complex
recruit chromatin modifying proteins (histone acetylases or deacylases)
What is the response element, function and protein clas of steroid receptor TF?
response element: HRE (hormone response element) or GRE (glucocortisol response element)
function: steroid repsonse
protein class: zinc finger
cortisol binds to TF in cytoplasm in hepatocytes and go to nucleus to bind to HRE
What is the response element (binding site), function and protein class of cAMP-response element binding (CREB) protein?
response element: CRE
function: response to cAMP
protein class: leucine zipper
What is the response element , function and protein class of peroxisoe proliferator activated receptors (PPARs)?
response element: PPREs
function: regulate multiple aspects of lipid metabolism; activated by fibrates (turn on PPAR alpha) and thiazolidinediones (PPAR gamma–decrease serum TG)
protein class: zinc finger
What is the effects of PPAR alpha and gamma?
PPAR alpha: metaboize fatty acids
-genes increase peroxisomes, which need triglycerides to work so decrease triglyceride levels
PPAR delta: store triglycerides in diposides
What is the response element, function, and protein class of NFkB (nuclear factor kappa-B)?
Response element: kB elements (in immune cells)
function: regulates expression of many genes in immune system (inflammation)
protein class: Rel domains
- glucocorticoids treat inflammation*
- –decrease signalling of NFkB signalling so no inflammation pathways turned on*
What is the response element (binding site), function and protein class of homeodomain proteins?
Response element: NA
function: regulate gene expression during development
protein class: helix-turn-helix
- homeobox gene/PAX gene–> homeodomain protein–>bind to and enhance and turn gene on*
- turn on during development –on euchromatin (fingers and toes) and then off (heterochromatin)*
What is the Klein Waardenburg syndrome?
Hox or PAX gene mutated –> limb abnromality
What is the result of thalidomide?
can cause limb abnormality
inhibits homeodomain protein binding to enhancer
*drug that use to treat morning sickness *
What are general transcription factors?
bind to promoter to allow RNA polymerase to bind and form initiation complex
include: TFIID with its TATA box binding protein subunit (TBP)–must bind to TATA box before RNA polymerase II can bind
What are specific transcription factors?
bind to enhancer regions or silencers an dmodulate formation of initiation complex–>regulate rate of initiation of transcription
*combination of specific TF in particular cell at particular time determines which genes will be transcribed at what rates *
specific TF are proteins–so expression can be cell-type specific
hormones can regulate activity of specific TF (ex. steroid receptors of CREB protein)
What are peroxisome proliferated activated receptors (PPARs)?
TF that bind DNA response elements (PPREs) and control lipid metabolism
activated by: fatty acids, Prostaglandin derivatives, fibrates, thiazolidinediones
How does thiazolidinediones improve insulin resistance?
interaction with PPAR alpha
What is Zellweger syndrome?
mutation in genes involved in peroxisome biogenesis
causes accumulation of long chain fatty acids and several unusually fatty acids, like hydroxylated and brancehd fatty acids
–defect in fatty acid efflux from peroxisomes
FEATURES: enlarged liver, ghih blood levels of Cu and Fe, vision problems
infants: failure to grow, mental retardation, abnormal muscle tone, multiple developmental abnormalities; die within first year
What are fibrates used to treat?
hyperlipoproteinemia with elevated blood triglyerides but normal cholesterol and LDL levels
–drug stimulates proliferation of peroxisomes and increases gene expression of lipoprotein lipase–>fatty acid oxidation pathway induction
(peroxisomes usually beta oxidize long and very long chain fatty acids; generate hydrogen peroxide)
What hormones bind to zinc finger proteins?
steroid hormones, thyroid hormones, vitamins A and D
What is cushing’s syndrome?
too much ACTH secretion–> increased cortisol
- hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia*
- –increased insuline–>turn on fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis *
**SYMPTOMS: **moon face, buffalo hump (TG storage), puruple striae
What is the gluconeogensis?
hepatic pathway that maintains adequate glucose in blood for tissues like brain and RBC during fasting and provides glucose during stress
–glucagon: secreted in response to hypoglycemia; membrane-assocaited receptor that increases cAMP concentration
–cortisol: secreted in response to stress; intracellular receptor–zinc-finger DNA binding protein





