Chest Radiology - slides 11-20 Flashcards
(12 cards)
What is this chest radiograph showing? Which lung is affected? Which lobe is affected?

- Atelectasis
- It means that an entire lobe of the lung has lost its air, causing all alveoli it that lobe to collapse
- The left lung
- Inferior lobe of the left lung
These symptoms are indicative of what?
- Sail sign
- Less alveolar
- Surface means Hypoxia
- Decreased Lung Volume
- CO2 remains normal
Atelectasis
Which structure is moving as a result of atelactasis?
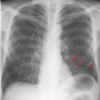
The left diaphragm
What does atelectasis mean? What does it look like on a chest radiograph?
- Consolidation of all or part of the lung due to a collapse of the alveoli
- Elevated diaphragm on the affected side
- Mediastinal shift towards the affected side
- Decrease in the spaces between the ribs
- Possible hyperinflation of the adjacent lung lobes or opposite lung
What pattern is produced with air density? Fluid density? Bone density?
Densities Seen on X-Ray
a. Air density – produces the darkest patterns
b. Fluid density – produces gray patterns
c. Bone density – produces the lightest patterns
What is this radiograph showing? This is an example of what?

- Complete Right Lung Collapse
- Atelectasis
What two methods were used to re-expand the lungs?

Re-expansion after bronchoscopy and removal of mucous plug
Is this a normal chest xray?

No, the diaphragm is pushed down.
This is an example of a localized, round opacity. What are the white arrows indicating? What are the black arrows indicating?

white arrows show a tumor; black arrow shows an enlarged node)
What is this chest radiograph showing? What does it mean? What is the typical shape?
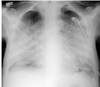
- Pulmonary Edema
- Interstitial fluid thickens the spaces between the alveoli and causes their collapse.
- Typical batwings (or butterfly) shape
Is this a photo of a resolving pulmonary edema?

In this film, one can appreciate that the cardiac border is now sharp and the edema is resolving
What does the collapse of alevoli lead to?
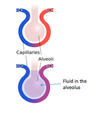
Atelectasis


