Muscloskeletal Radiology - slides 1-12 Flashcards
(12 cards)
What view is this and what structures do you see?
(from superior to inferior)

- Clavicle
- Acromion
- Coracoid
- Glenoid fossa
- Greater tubercle
- What view of the normal shoulder is this?
- Identify the following:
- Clavicle
- Greater tubercle
- Coracoid
- Head
- Surgical Neck
- Neck of scapula
- Acromion


How is a normal rotator cuff present in a coronal MRI scan of a normal shoulder?
Is present as a thick, black structure just above the humeral head
What are the 4 rotator cuff tendons?
- Supraspinatus
- Subcapularis (front right)
- Infraspinatus (top, back, left)
- Teres minos (lower, back, left)

How can you detect a supraspinatus tear?
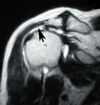
The normal, thick, black tendon just above the humeral head is absent. There is a white area above the humeral head and this represents fluid resulting from the rotator cuff tear.
What kind of injury is this?

This is a SLAP tear (superior labrum anterior posterior)
This is an injury of the labrum of the shoulder. The labrum is a rin of fibrocartilage that surounds he edge of the articular head of a bone.
What kind of tumor do you see in this picture?
What is a main characteristic of this disease?

Osteosarcoma of proximal head of the humerus.
Moth-eaten border of the bone. No ossification on X-ray.
What can you see in this picture?

This is an anterior dislocation of the humerus.
The head of the humerus resides in front of the glenoid
What kind of injury is this?

Posterior dislocation of the humerus.
Head of the humerus resides behind the glenoid fossa
Which dislocation of the humerus is more common, anterior or posterior?
Anterior dislocation is more common
What kind of fracture is this?

Fracture of the proximal humeral head.
In what parts of the humerus can you have a two part shoulder fracture?
- Neck
- Greater tuberosity
- Leser tuberosity



