Muscloskeletal Radiology - slides 33-44 Flashcards
(26 cards)
Name this type of fracture.

Colles fracture.
What type of fracture is a posterior displacement, where the wrist slides over the arm?
Colles Fracture

Name this type of fracture.

Smith Fracture.
Fracture that is displaced ventrally, where the wrist (distal radius) slides underneath the arm. Also known as a “reversed Colles’ fracture”.
Smith Fracture.
Fracture of the 5th metacarpal bone.

Boxer fracture.
This fracture is difficult to initially diagnose, it can take up to two weeks. The patient experiences pain in the Snuffbox (between the base of the thumb and the radius; depressed area best seen with abduction of thumb).

Scaphoid fracture
Damaging the anatomical _________ causes damage to radial artery and scaphoid bone.
Snuffbox.
Name structures 1, 2, and 3 of the hip and pelvis.
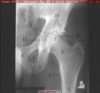
- Pubic symphysis
- Obturator foramen
- Ischial tuberosity
Name structures 4, 5, and 6 of the hip and pelvis.

- Femoral neck
- Femoral shaft
- Lesser trochanter
Name structures 7, 8, and 9 of the hip and pelvis.

- Femoral neck
- Greater trochanter
- Lunate surface of the acetabulum
Name structures 10, 11, and 12 of the hip and pelvis.

- Acetabular fossa
- Ileopectineal line
- Fovea of femoral head
What type of image is this?

Normal AP pelvis
This fracture occurs when the head of the femur is driven into the pelvis. This fracture, along with isolated fractures of the ilium, ischium, pubis, or ilium are stable.

Acetabular fracture
In this type of fracture, the ring is broken in two places (the ring is open). This causes disruption of the pubic symphysis.
These fractures occur in pubic symphisis or sacrioiliac joints.

Open book fracture.
Is this a normal hip bone or a dislocated hip bone?

Normal hip bone.
Hip dislocations are either anterior or posterior. This particular dislocation comprises the majority of traumatic dislocations.

Posterior hip dislocation
In approximately 90% of hip dislocation patients, the thighbone is pushed out of the socket in a backwards direction. This dislocation leaves the lower leg in a fixed position, with the knee and foot rotated in toward the middle of the body.
Posterior hip dislocation
The arrow in the MRI is pointing to what?

Trochanteric Bursitis
This is the most common bursitis of the hip. Inflammation of the bursa, which lies over your femur.
Trochanteric Bursitis
This image is a fracture of the?

Hip
This image shows ______, which is death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply. Also called osteonecrosis, avascular necrosis can lead to tiny breaks in the bone and the bone’s eventual collapse. The hip is the joint most commonly affected by this.

Avascular necrosis
In a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the thighbone (femur) fits firmly into the socket, which is part of the large pelvis bone. In babies and children with this condition, the hip joint has not formed normally. The ball is loose in the socket and may be easy to dislocate.
The socket (acetabulum) is shallow, meaning that the ball of the thighbone (femur) cannot firmly fit into the socket. Sometimes, the ligaments that help to hold the joint in place are stretched. The degree of hip looseness, or instability, varies among children with this condition.

Congenital hip dislocation
Developmental Hip Dysplasia (DDH)
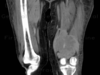
This image is a fracture of the ___. .

Femur. Midshaft: importance of good films, which include both joints, and an AP and lateral view.
The longest and strongest bone in the body, takes a lot of force to break it. Car crashes are the number one cause of these fractures.
Femur