Chest Radiology - slides 2-10 Flashcards
(28 cards)
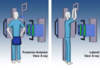
Upright _______ view X-ray of chest the plate is in front and the beam comes from the back. The direction of the beam is from the back to the front. X-rays hit it first, spine gets diluted out in the picture and the cartilage sillhohette appears, which is much easier to read. Will push your shoulders right against the plate

PA (Posterior Anterior) View X-ray
_______ view X-ray: arms are upward holding on.
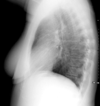
Lateral view X-ray
The patient is positioned to face the X-Ray ______, with his/her arms out of the projectory of the beam.
plate
In a PosteroAnterior (PA) Chest X-ray, the bones of the spine are further away from the plate, so their density is diffused and does not obscure the ______
mediastinum.
Sick, bedridden patients often require a bedside film, an ______ view with their back against the plate. In this kind of projection, the heart is magnified.
AP (Anterior-Posterior)
In an AP X-ray film, the heart is grossly ___, so if you want to measure size of heart this would not be the proper way.
Magnified
When reading films: Make sure that
A: It’s the correct ____
B: It’s the correct _______ (if prior films are available, use them for comparison)
C: It’s the correct ______ (R vs L may be the patient’s R and L, or the film’s R and L)
patient, film, side
If ____ X-ray films are available you can pull them up in the computer to compare them.
prior
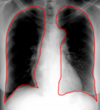
This is a normal ______ X-ray view (woman patient) of the chest.

PA
This is a normal ______ X-ray view (woman patient) of the chest.
Lateral
In PA and lateral chest X-rays, the heart shows up very well because the ________ isn’t so bright that it obscures the heart.
vertebral column
NORMAL PA/LATERAL CXR
A satisfactory CXR includes all _____ribs, the diaphragm, both clavicles.

24
NORMAL PA/LATERAL CXR
The ____ should be of optimal penetration.
The ___ follows the periphery of the film first, observing soft tissues and rib contours one by one, then the diaphragm.
Next, the ____ of the mediastinum.
Lastly, the ___ ___.
film, eye, contours, lung fields
When reading an X-ray, it is important to start reading from the ___ and go inwards.
sides
When reading a chest X-ray, observe soft tissues and rib contours one by one, then go to the ____.
diaphragm
When reading a chest X-ray, the ___diaphragm always higher than ____ diaphragm because the liver pushes the R diaphragm up. On left side, stomach and spleen are not that big.
right, left
Do not need to memorize but for your information:
The main regions where a chest X-ray identifies problems may be summarized as ABCDEF by their first letters:
- Airways, including hilar adenopathy or enlargement
- Breast shadows
- Bones, e.g. rib fractures and lytic bone lesions
- Cardiac silhouette, detecting cardiac enlargement
- Costophrenic angles, including pleural effusions
- Diaphragm, e.g. evidence of free air, indicative of perforation of an abdominal viscus
- Edges, e.g. apices for fibrosis, pneumothorax, pleural thickening or plaques
- Extrathoracic tissues
- Fields (lung parenchyma), being evidence of alveolar flooding
- Failure, e.g. alveolar air space disease with prominent vascularity with or without pleural effusions
On a chest X-ray, Start counting ribs – best counted from ____.
edges.
Chest X-rays miss a lot of fractured ribs. ____ scan does not.

CAT
CAT scan is $3500 and chest X-ray is $1200. Once you have evaluated the ribs, clavicle, and apices, make sure no mediastinum shift and then look at the ____. Every single part of the lung is investigated.
diaphragm
If the right atrium is distended (big) it is possible that there is a problem with the ______. You may have a pulmonary artery problem. This will cause ventricle and R atrium to enlarge.

bicuspid valve
R atrium sits right on top of the ______. Above that there are two lines – superior vena cava and the one you see against contour of air present in the lungs is the ascending aorta – swings to the R, crosses the mediastinum and becomes posterior after making an arch of the aorta.
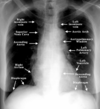
diaphragm
Aortopulmonary window is supposed to have small ___ ___. Normally lymph glands are <1 cm. we have hundreds of them in mediastinum. Not normally big enough to fill the space so that the air from the left lung is not good enough to overcome that area that is full. If aorta pulmonary window is full then there is a problem with nodes in the mediastinum.

lymph nodes
What part of mediastinum would this be (right below the aorta) = _____ mediastinum because the angle that separates the junction between manubrium and body of the sternum –above that superior mediastinum, below that is inferior mediastinum. Angle on clavicles is the notch so the angle is there.

INFERIOR



