Derm3 Flashcards
(48 cards)

Pompholyx - dishydrotic eczema
Young adults (more F)
FHx of atopic eczema
Some report hyperhidrosis
RF’s - contact with irritants, genetics, drug reactions
RECURRENT episodes of blisters on palms and soles, burning and itching,
Treat: Avoid irritants
Wet dressings/soaks
Potent steroid (mometasone furoate 0.1%)
Oral corticosteroid for 3 weeks

Asteatotic eczema
Elderly, hypothyroid or drugs (Statins/diuretics)
Alleviate dry skin - soap substitute
Emmolients and moisturisers
Hydrocortisone 1% ointment
(more potent if not responding)

Erythema marginatum
annular erythema to Trunk, upper arms and legs
Non itchy, non painful
What are the causes of erythema nodosum
- Sarcoidosis (CXRay)
- Streptococcal infections (ASOT)
- TB
- Chron’s disease
- Pregnancy
- Drugs - tetracyclines, OCP
- Malignancy
How do we treat erythema nodosum
- Treat the cause
- Rest, elevate,
- Ibuprofen 400mg tds prn if acutely painful
- If severe prednisolone 0.75mg/kg daily for 2 weeks
- Often settles spontaneously over 3-8 weeks
Tests for Erythema Nodosum?
FBE, CXR, ASOT, Mantoux, ESR/CRP
Clinical features of erythema nodosum

What is erythrasma? How does it present
This is a skin fold rash - well defined PINK or BROWN patches with fine scaling and superficial fissuring. Mildly itchy
APPEARS CORAL PINK UNDER A WOODS LAMP
Treat with fusidic acid 2% BD for two weeks
Prevention - antibacterial soap
Demographics - diabetes, obesity, warm climate

What is a felon? How is it treated
This is a an abcess of the pulp of the fingertip.
Multi or single compartment abcess of the pulp.
Predisposed by thorn, wood splinter, minor cuts, infection from a paronychia
Treat with incision and decompression of abcess
Administer antibiotics with sensitivity to MRSA
eg clindamycin


A digital myxoid cyst or mucous cyst is a pseudocyst- not surrounded by a capsule
presents as shiny pappule on a finger or a toe - close to the nail
Treatment
- repeated firm pressing
- squeezing out of contents
- cryotherapy
- steroid injection

Glomus tumour
nail bed/finger tip or palm
within the glomus body which helps with thermoregulation
EXTREMELY PAINFUL - esp following temperature or pressure
Excisional biopsy
Remove at same time ;)
Causes of flushing?
Commonly - women in menopause (consider HRT)
ROSACEA (will have erythema, papules, pustules)
ETOH
Spicy food
Stress
Phaeo
drugs - calcium channel blockers, sildenafil, nicotinic acid
Treat the cause
If want treatment - Propranolol 10mg bd

Folliculitis
Mupirocin ointment BD topically for five days
Recurrent boils:
Swab for MCS
3% Hexaclorophene body wash daily
Mupirocin Nasal ointment 2%

Wetsuit folliculitis
Same as spa pool
folliculitis where costume has been - a few days after
Treatment
Gentamycin Cream
Polymyxin B spray
Oral ciprofloxacin

spa pool folliculitis
folliculitis on trunk after being in spa or where costume has been - a few days after
PSEUDOMONAL
Treatment
Gentamycin Cream
Polymyxin B spray
Oral ciprofloxacin
What is pseudofolliculitis barbae and folliculitis barbae
SHaving rash
Folliculitis barbae - painful pustules
Pseudofolliculitis - foreign body inflammatory rash around ingrown hairs in beard
Advice:
if possible let the beard grow out to avoid ingrown hairs
Moisturise with a lotion containing glycolic acid
Shave in the direction of the follicle (not against)
Use single blade disposable razors
Treatment
folliculitis - mupirocin 2% bd
pseudofolliculitis - Benzoyl peroxide 5% gel
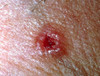
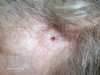
What margins should you keep in a Non melanomatous skin cancer biopsy?
2-3mm for well defined - less than 10mm lesion
4-5mm for larger than 10mm or poorly defined lesions.
If lesion is too large for excisional biopsy
do 1) partial b) refer to specialist
If doing a partial biopsy for NMSC what would you do?
For a Bowns or superficial BCC - do a partial shave biopsy as they are thin lesions
Treatment options for a NMSC which can’t be treated with excision
- Curretage and diathermy - superficial BCC and bowens on body and limbs
- Liquid nitrogen - superfical lesions body and limbs
- Imiquimod - for biopy proven superficial BCC where surgery cant be used
- Fluorouracil approved for treatment of Bowens
- Radiotherapy - For Older people over 70 - excellent cure rate - 6 weeks - 5 days per week.
How would you manage SCC in ears, eyes, nose or lips
DANGER AREAS
needs excisional biopsy not creams or cryo
But in ppl over 70 - you can do radiotx for bcc and scc in head and neck
Other areas of body - not head and neck -
Superfical proven BCC in areas of body (Apart from head an neck)
either - curretage and diathermy, imiquimod or surgical excision
Bowens disease management ?
Fluorouracil, surgery or curettage and diathermy
What happens if there’s perineural or perivascular invasion of a NMSC?
REfer to specialist
higher risk of metastasis