ENT3 Flashcards
(20 cards)
What are indications for Middle ear ventialation tubes (grommets)?
persistent middle ear effusion for over 4 months with:
conductive deficits
significant hearing loss
known language delay
learning/intellectual problems
visual impairment as well as hearing loss
Damage to TM
What is recommended if a child needs a second set of middle ear ventilation tubes?
Adenoidectomy
Adenoidectomy does not prevent recurrent AOM
What advise would you give a family with a child who has persistent symptomless ear effusion at 3 months
Family education - advise about potential hearing loss (usu around 25db) and the need to organise hearing tests.
Recommend ENT referral for consideration of middle ear ventilation tubes if Persistent OM coincides with TM damage, behavioural or hearing difficulties,
Audiological - monitor for any delay in language development - if hearing loss is 20-35 db the child will benefit from classroom sound field amplification and enhanced communication strategies (get close, speak clearly, check understanding)
What is a cholesteatoma? Management?
Sac of keratinising squamous epithelium arising from a perforation in the periphery of the tympanic membrane.
As it expands it can damage adjacent structures such as TM, ossicles and cochlea.
Needs surgical management

How would you treat discharge in a patient with middle ear ventilation tubes?
- Dry aural toilet 6 hourly
- Ciprofloxacin 0.3% 5drops bd till dry
Antibiotics for otorrhea
For first six weeks
AFTER SIX WEEKS its CSOM - so just cipro 0.3% 5 drops bd
and dry aural toilet q6hrly
and REFERRAL TO ENT SURGEON to see if CSOM is atticoantral or tubotympanic
How would you know if CSOM was atticoantral
Discharge is scant, FOUL smelling, Purulent
How would you know if CSOM was tubotympanic
Discharge is profuse, non foul smelling and mucoid
Nasal polyps management?
Intranasal steroids are first line
Surgical referral if obstruction occurs
Risk factors for otitis externa
Allergic skin conditions
Ear trauma
Water in the ear
Debris in the ear
hearing aid
Q tips
Organisms in Otitis externa
Pseudomonas
Staph aureus
Fungal - aspergillus, candida
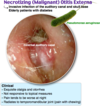
Exquisite otalgia and otorrhea, elderly/diabetic/immunocompromised
not responsive to topical ear drops
What is bullous myringitis

What is dry aural toilet?
Dry mopping the ear canal with rolled tissue spears or similar 6hourly until external canal is dry, Can also be achieved by external suction
Management of otitis externa
- 6hrly Dry Aural toilet
- Swab M/C/S
- Sofradex ear drops 3 drops TDS for seven days (pump the tragus (by repeated presssing on it without causing pain) for 30 seconds after instilling drops)
- Paracetamol 15mg/kilo up to max of 1g qid orally daily
- Avoid water entering the ear for two weeks (no swimming)/shower cap
- Prevention
- keeping ear dry - use of ear guards/swimming and shower caps
- If water enters while swimming can use aqua ear (Acetic acid) drops
- Avoid putting anything into the ear as this may cause infections
If there is a concern about tympanic perforation in otitis externa which drops would you use
Ciprofloxacin on their own 0.3%
How would you treat a fungal otitis externa
Flumethasone pivilate/cliquinol drops for two weeks
Clinical features of otitis externa
- Itching followed by pain (70%),discharge and deafness
- swelling
- erythema
- TM is granular or dull red
- Discharge - offensive - bacterial; non offensive pale cream - candida fungal; black dots - aspergillus fungal
What investigations for a suspected malignant otitis externa
REFER urgently first to ID (Iv abx will be needed)
CT temporal bones
Bone scan to document osteomyelitis
Gallium scan to track and document disease
How would you manage a localised otitis externa? (eg a boil associated with a hair follicle)
Flucloxacillin 12.5mg qid for five days
Immediate sensitivity to penicillin
Clindamycin 450mg TDS for five days
10mg/kilo


