ICM - Data stuff! Flashcards
(158 cards)
What are the four cardiac arrest rhythms?
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Pulseless ventricular Tachycardia
- Asystole
- Pulseless Electrical Activity
What are the two shockable Cardiac Arrest Rhythms?
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Pulseless ventricular tachycardia.
Which type of cardiac arrest rhythm is this?

Asytole (not-shockable)
What kind of cardiac arrest rhythm is this?

Pulseless electrical activity. (Not shockable)
What kind of cardiac arrest rhythm is this?

Pulseless ventricular tachycardia. (Shockable)
What kind of cardiac arrest rhythm is this?

Ventricular fibrilation.
Which valve does each of these points of auscultation listen to?

Green - Aorta
Red - Pulmonary
Yellow - Tricuspid
Blue - Mitral
All Prostitutes Take Money
The ‘lub’ of the heart is caused by the closing of which valves?
Tricuspid and mitral, at the start of ventricular systole.
The ‘dub’ of the heart beat is caused by the closing of which valves?
Aortic and pulmonary valves, during diastole.
What are some of the causes of systolic murmur?
Aortic valve stenosis
Mitral regurgitation
Pulmonary valve stenosis
Tricuspid regurgitation
What are some of the causes of a diastolic murmur?
Mitral stenosis
Tricuspid stenosis
Aortic regurgitation
Pulmonary regurgitation
What is one of the main causes of continuous murmur?
Patent ductus arteriosus.
Why does a patient need to be upright for a chest X-ray?
So that free air can be seen under the diaphragm, pneumoperitoneum.
Which type of X-ray will show an innacurate view of the heart?
AP - divergence of the x-ray beams show an enlarged heart.
What is the normal cardiac-thoracic ratio?
<50%
How should a chest X-ray be performed?
- PA
- Inspiration
- Erect
- No rotation
What are the borders of the heart visible on an x-ray?
- Left Ventricle
- IVC
- Right Atrium
- SVC
- Aortic knuckle
- Left auricle
What can you see on this X-ray?

1) Right Hilum
2) Left Hilum
3) Right hemidiaphragm
4) Left hemidiphargm
5) Gastric bubble
What can you see on this x-ray?

A) Trachea
B) Carina
C) Right Clavicle
D) Left Ventricle
E) Aortic knuckle
What can you see in this x-ray?

A)
B) ECG lead
C) Endotracheal tube
D) Nasogastric tube
E) Surgical staples
F)
What are the four densities to look at in abdominal X-rays?
1) Gas
2) Fat
3) Soft Tissue
4) Bone
Why is the liver visible on an abdominal X-ray?
It is denser than the retroperitoneal fat around it, so it is a darker shade of grey.
What five abnormalities can we see on an abdominal radiograph?
1) Foreign bodies
2) Perforation
3) Kidney stones
4) Bowel obstruction
5) Abdominal masses
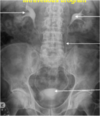
What can you see in this abdominal X-ray?

Staghorn calculus in left kidney.