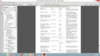
Lecture 3 Flashcards
(6 cards)
What are the 7 concepts of Motor Development?
- Sequential - Based on what came before, Rates of skill acquisition vary, pateus and spurts,
- Overlapping - similar to sequential, child doesn’t perfect skill before getting to next one
- Cephalo-Caudal - Neck control before trunk control
- Proximal-Distal - Proximal joints to distal joints, Midline to periphery
- Mobility-Stability - movement precedes posture
-
Sensation - neonates first functional movements reflexively cued, Touch cues precede visual cues,
Volitional movements emerge, Sensory information matures as experiences change - Dissociation - movement of one part of the body separate from another. ex: Reciprocal creeping and belly crawling is dissociation
What is the first volitional movement?
Why is this important?
- Head lifting in the prone position
- Necessary to begin mobility skills, may need prone tolerance program (STNR can help facilitate)
What are some general milestones for motor development?
Milestone age
Head control 4 months
Rolling 6-8
Sitting 8
Creeping 9 months
Cruising 10
Walking 12 months
What are some more specific milestones for:
2 year old?
3?
5-6?
Adolescent?
Adult?
2) reciprocal arm swing, heel srike in gait, stand on 1 foot for 3 seconds, flight in running, “marking time”
3) up and down stairs reciprocally, running with better balance, hopping, climbing a slide ladder
5-6) ride a bike, skip alternating, stand on one foot 8-10 secs
Adol) skills develop based on experience, puberty effects
Ad) change in movement patterns
What are the steps involved with prehension?
- *Visual regard** – visually attend to object (children before 1 yo do not have depth perception)
- *Reach** – preshaping hand to grasp object
- *Grasp** – contact and close on object (power grip, precision, etc)
- *Manipulation** – move the object within your hand (stereogenesis: the ability to recognize w/o visual stimulus)
- *Release** – How object leaves the hand
Prehension Development Chart p.321