M2. U2. RF. Flashcards
Animal nutrition (129 cards)
a round ball of chewed food that is pushed in the direction of the oesophagus during swallowing
food bolus
functions of the pancreas
- secretes pancreatic juice and enzymes
- secretes insulin and glucagon
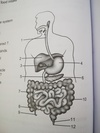
8

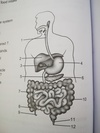
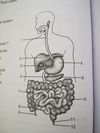
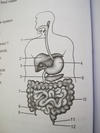
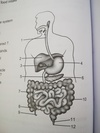
ileum
2
longitudinal muscles
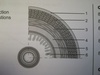
Stomach structure.
- sickle shaped organ below diaphragm
- thick, muscular wall
- opening to oes. closed with cardiac sphincter
- opening to small intest. closed with pyloric sphincter
process in nutrition when food is taken in and enters the alimentary canal
ingestion
process in nutrition when the end products of nutrition are absorbed into the bloodstream
absorption
12

anus
Absorption of water
- passive transport (osmosis)
- capillaries
jejunum
middle part of small intest.
the structures on the tongue that ensure that it can function as a taste organ
taste buds
structures in the small intestine mainly responsible for the absorption of nutrients
Villi
the harmful effect of excess alcohol on The Unborn foetus
foetal alcohol syndrome
group of enzymes involved in the chemical digestion of proteins
proteases
group of enzymes involved in the chemical digestion of carbohydrates
carbohydrases
the maintenance of a constant internal environment in the body
homeostasis
the three parts of the small intestine
duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
end product of protein digestion
amino acids
5

duodenum
Carnivore volume of food intake?
Low. Meat is high in protein and fat.
a metabolic disease characterised by high glucose levels in the blood
diabetes mellitus
Duodenum
- 1st part of small intest.
- connected to gall bladder, pancreatic duct
process in nutrition when undigested remains are removed from the body
Egestion