MCM_Final_TBL12 Flashcards
(29 cards)
Globular proteins
- spherical (hydrophilic surface with hydrophobic core)
- soluable in H20
- sensitive to pH and heat

Function of Globular Proteins
-
storage of ions and molecules
- myoglobin & ferrin
-
transport of ions and molecules
- hemoblogin & serationin transporter
-
defense against pathogens
- antibodies & cytokines
-
muscle** **contraction
- actin & myosin
-
catalysis
- chymotripsin & lysozyme
Globin Gene Families
-
gene family = set of similar genes, formed by duplication of a single original gene & typically with similar biochemical functions.
- non-identical primary sequences
- can be clustered or dispersed
- (ex) hemoglobin
-
heterotetrameric protein made of two subunits from two clustered gene families
- 2x unit of α-globin = on Chrm. 16
- 2x unit of β-globin; located on Chrm. 11
-
heterotetrameric protein made of two subunits from two clustered gene families
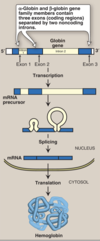
Globulin Gene Switching
- produces a variety of different hemoglobin tetramers throughout development
Primary Hb Species (2)
- HbF
- during fetal development
- 2 Adult α2-subunits
- 2 Fetal β-subunits
- during fetal development
- HbA
- major form shortly after birth through adulthood
- 2 Adult α2-subunits
- 2 Adult β-subunits

Myoglobin vs Hemoglobin
- hemoglobin = heterotetramer
-
myglobin = monomer (abundent in muscle)
- designed to store O2
Fe2+-protoporphyrin IX (9) prosthetic grounp
- binds O2 to BOTH proteins

Oxygen Binding in MYOGLOBIN
- α- helical SECONDARY & TERTIARY structure
- single heme group = binds 1 O2 molecule
- O2 binds to ferrous iron on heme group
- in the absence of allosteric interactions, the O2 binding curve is hyperbolic

Allosteric Regulator (Effector)
allosteric regulation of hemoglobin depends on many allosteric effectors
- molecule that binds to a protein and induces a conformational change that alters:
- affinity for a substrate (i.e O2) (“K effect”)
- the Vmax of enzyme (“V effect”)
- OR both (“V/K effect”)

H+ & CO2 are …
NEGATIVE allosteric effectors of O2 binding in HB
- ↓ O2 affinity for hemoglobin = shifts curve TO RIGHT
-
↑ efficiency for O2 unloading in tissues
- facillitates the H+ & CO2 transport from tissues → lungs

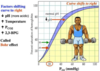
Myoglobin vs Hemoglobin Curve Comparison
Note: O2 Binding to Myoglobin-Hemoglobin Curves = Substrate- Enzyme Velocity Curves
- Due to monomeric structure, myglobin has hyperbolic curve
- Due to complex, tetrametic structure, hemoblogin has SIGMOIDAL COOPERATIVE binding curve

P50
- partial pressure of oxygen yielding 50% saturation
- “partial pressure of oxygen when hemoglobin is 50 % saturated with oxygen”
Hyperbolic vs Cooperative Binding
Myoglobin
- ↓ P50 = ↑ O2 affinity…. leads to hyperbolic binding of myoglobin
- when O2 is ↓ (i.e during exercise), myoglobin will release O2 to maintain activity for long time
Hemoglobin
- cooperative binding of Hb = efficiency in Loading O2 in Lungs & unloading in tissues
Hb’s Squential Cooperative O2 Binding
-
binding O2 in one subunit induces a conformational change that is _partially_ transmitted to _adjcacent_ subunits
- ↑ O2 affininty in adjacent subunits

Conformational Change Trigger
- trigger = orientation of Fe2+ in protoporphyrin ring
- iron’s movement is transmitted to the Hb subunit via histidine axial ligand
- in deoxyHb, the Fe2+ and porphyrin ring are not* perfectly *aligned
- in oxyHB, the ring becomes straighter pulling in the proximal histadine axial ligand

R vs T States of Hb
- T = Tense state
- ↑ interactions = ↑ stability
- ↓ O2 affinity
- R = Relaxed state
- ↓ interactions = ↑ flexibility
- ↑ O2 affinity
- O2 binding triggers a T → R conformational change by breaking ion pairs between the α1-β2 interface
Fetal Hemoglobin (HbF)
-
HbF has ↑ O2 affinity than HbAdults
- = LEFTWARD shift in the oxygen binding curve
- why?
- HbF needs to work with the O2 lvls the placental interface

Allosteric Effectors: Oxygen
-
POSITIVE allosteric effector for its own binding
- basis for subunit cooperativity
- BUT ALSO NEGATIVE allosteric effector for CO2 & H+ binding
- why? that ↑ efficiency of H+ & CO2 unloading in lungs
AKA the Bohr Effect = *reciprocal relationship* between O2 & CO2/H+ binding
Curve Shift Trends
HbA2
- synthesized in the adult,
- although at low levels compared with HbA
Globin Gene Organization
- α-gene cluster on chromosome 16 contains two genes for the α-globin chains
-
single gene for the β-globin chain is located on chromosome 1
- ζ gene, is expressed early in embryonic
- two γ genes (Gγ and Aγ that are expressed in HbF)
- δ gene found in the minor adult hemoglobin HbA2.
Hemoglobinopathies
group of genetic disorders caused by production of a structurally abnormal hemoglobin molecule OR synthesis of insufficient quantities
qualitative hemoglobinopathy
- altered A A sequence i.e sickle cell
quantitative hemoglobinopathy
- thalassemias
- decreased production of normal hemoglobin
Sickle Cell Anemia (Hemoglobin S disease)
- (a point mutation) in the gene for β-globin:
- replacement of the charged glutamate → nonpolar valine
- ccurs primarily in the African American population
- autosomal-recessive disorder
- infant does not begin showing symptoms of the disease until sufficient HbF has been replaced by HbS
- hyperbilirubinemia



