MCM_Final_TBL9 Flashcards
(28 cards)
3 Types of Human Genetic Disorders
- Single Gene/Mendelian Disorders
- results from mutation in single gene
- Large Scale Chromasomal Disorders
- results from structural or numerical mutation in chromasomes
- Mutagenic Disorders
- results from polymorphism and environmental factors
Independent Assortment
BETWEEN
- he looked at two pairs of contrasting traits (yellow or green and round or wrinkled)
- Genes assort independently during gamete formation
- All possible gamete combinations form with equal frequency
I.E ONE trait for being round vs wrinkled is independent of ANOTHER trait for being green vs yellow. (THE SORTING OF TRAITS IS INDEPENDENT OF EACH OTHER)
= genetic variation
Independent Segregation
Independent Segregation
- paired sister chromatids are seperated independently
Point Muations
- Deletions or insertions of a single base
- Substitution of base (ie A → T)
- Silent mutation: no different in phenotype
- Nonsense: mutation makes a STOP codon
- Missense: makes a DIFFERENT AA
Trinucleotide-repeat mutations
insertion of many copies of a codon (usually containg G/C)
- loss of gene function
- toxic gain of function (via changes in protein structure)
- toxic gain of function (via mRNA)
Diseases
- Fragile X Syndrome
- Fragile X Tremor Ataxia
- Fragile X Associated Ovarian Insuffiency
- Friedreich Ataxia
- Huntington
Tay-Sachs Disease
- four-base insertion in the hexosaminidase A (HEXA) gene = frameshift mutation
- makes different AA dequence = defect in protein function

Fragile X Syndrome
- CGG Triplet
- transcriptional silencing
- loss of protein function
Fragile X Tremor Ataxia & Fragile X Ovarian Insufficiency
- CGG Triplet
- transcriptional DYSREGULATION
- ACCUMULATION of toxic mRNA
Friedreich ataxia
- GAA triplet
- transcriptional silencing
- loss of function
Intro to Huntington Disease
- CAG triplet
- polyglutamine expansions + misfolding
- toxic gain of function
Huntington’s Disease (in depth)
- autosomal DOMINANT w. age dependent penetrance
- gene effected: HTT encoding Huntington protein
- repeat of CAG +40
- greater repeats = earlier onset
- repeats = long misfolded polyglutamine = protein clogs (nuclear inclusions) = neurodegeneration
Fragile X Syndrome (in depth)
- X-linked with INCOMPLETE PENETRANCE
- gene effected: familial mental retardation FMR1 gene on X chromosome
- repeat: CGG
- 55-200 repeats = lowkey effected / 230+ repeats = full effected
- in the abscense of folate, the X becomes fragile and breaks
-
most common cause of intellectual disability IN MALES
- SECOND TO Down’s overall
Codominance
- neither allele is dominant
-
both alleles expressed in heterozygotes
- EX) ABO blood groups or pink flowers
Epistasis
-
gene interaction:
- expression of one gene makes or modifies the effect of another
- Ex) Bombay Phenotype: Type O blood
- DOUBLE PUNNET SQUARE: albinism + fur color genes
X-linked
- Inheritance pattern is different depending on which parent carries the trait.
- Mother passes to all sons & ½ of daughters
- Fathers passes to all daughter & NO SONS
- (ex) Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Mitochondrial Heredity
- Mitochondrial DNA = double-stranded circular DNA inherited from mother
- mtDNA susceptible to mutations: No histones in mtDNA for protection, sad DNA repair mechanism, high concentrations of reactive oxygen bc of cell respiration
Diseases:
- Myoclonic epilepsy and ragged-red fiber disease (MERRF)
- Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON)
- Kearns–Sayre syndrome (KSS)

Autosomal dominant
- always appear in each generation.
- Affected individuals all have affected parents.
- appear equally in both sexes

Autosomal recessive disorders
- typically skip generations.
- appear equally in both sexes.

X- Linked Dominant VERY RARE
- For affected fathers, all their daughters will express (sons all fine)
- For affected mothers:
- ½ of sons of affected heterozygotes mothers will express the phenotype.
- All sons of affected homozygotes mothers will express the phenotype
Examples include Vitamin D–resistant rickets and Alport syndrome

X-linked Recessive
Females will very rarely express but are carriers.
- 50% of male offspring will be affected
- 50% of female offspring will be carriers
Often only affected males arise in the pedigree of an X-linked recessive disorder.
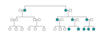
mtDNA Disorders
- b/c only the maternal mtDNA is passed, all the children of a female who has a mtDNA mutation will inherit the mutation.
Effected male will pass it to none of his children.



