Neurovascular of Lower Limb Flashcards
(52 cards)
where does the aorta bifuricate into common iliac artery?
- L1
- L2
- L3
- L4
- L5
where does the aorta bifuricate into common iliac artery?
- L1
- L2
- L3
- *- L4**
- L5
1-4?
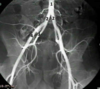
1 - aorta
2 - common iliac artery
3 - interal iliac artery
4 - external iliac artery
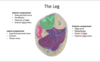
which three arteries branch off the internal iliac artery? [3]
which out of ^^ are medial compartment of thigh?
which out of ^^ are posterior compartment of thigh?
from which artery does the superior gluteal artery arise from? [1]
internal iliac artery –> superior gluteal artery
internal iliac artery –> inferior gluteal artery
internal iliac artery –> obturator artery
superior & inferior gluteal: posterior region
obturator: medial region
superior and inferior gluteal artery relate to which muscle? [1]
superior and inferior gluteal artery relate to which muscle? [1]
piriformis !

where does external iliac artery –> femoral artery? [1]
where do u palpate for femoral artery? [1]
where does external iliac artery –> femoral artery? [1]
at inguinal ligament
where do u palpate for femoral artery? [1]
mid inguinal point
which artery is commonly used to gain access to abdominal aorta?
- descending aorta
- femoral artery
- hepatic artery proper
- common iliac artery
which artery is commonly used to gain access to abdominal aorta?
- descending aorta
- *- femoral artery**
- hepatic artery proper
- common iliac artery
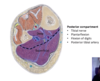
what are the three borders of the femoral triangle? [3]
which structures do we find in femoral triangle? [3] - correct order pls from lateral- medial
what are the three borders of the femoral triangle? [3]
inguinal ligament
sartoria
adductor longus
which structures do we find in femoral triangle? [3] - correct order pls !!
femoral nerve, artery, vein

what is the first branch of the femoral artery?
what does ^ lead into? [2]
what are the branches of the femoral artery?
femoral artery –> profunda femoris: –> medial circumflex femoral artery
femoral artery –> profunda femoris: –> lateral circumflex femoral artery
both supply the head of the femur
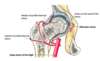


at what stage does femoral artery –> popliteal artery? [1]
at what stage does femoral artery –> popliteal artery? [1]
after going through the adductor hiatus

popliteal artery divides into ? [2]
popliteal artery divides into ? [2]
- *- posterior tibial artery - gives off fibular artery laterally
- anterior tibial artery**
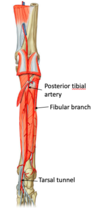
which artery
antierior tibial artery –> which artery?
antierior tibial artery –> dorsalis postieror artery
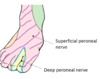
dorsalis pedis pulse can be found lateral to which tendon? [1]
dorsalis pedis pulse can be found lateral to which tendon? [1]
extensor hallucis longus (big toe tendon)
superficial veins of legs?
what do they drain into?
small / short saphenous vein –> popliteal vein
great saphenous vein –> femoral vein

why do superficial veins at greatest risk of varicous? [2]
why do superficial veins at greatest risk of varicous? [2]
- **outside of fascia - less muscle compression
- further to run / agaisnt gravity**

dorsalis pedis artery

arcuate artery
all nerves from the lower limb come from where? [1]
all nerves from the lower limb come from where? [1]
lumbosacral plexus !!
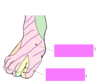
label the correct dermatomes xox

S1 - small toe AND base of most of foot - STAND ON S1 !

how do u remember dermatomes of lower limb? L3-L5 & S1-S4?
L3: knees
L4: down to the floor
L5: big toe
S1: stand on S1
S2: lie on
S3: sit on
S4: wipe

whats a myotome?
same as dermatome - but for motor movement
lumbosacral plexus:
which major nerves come from the lumbar plexus? [3] what are nerve roots?
which major nerves come from the lumbar plexus? [3]
femoral nerve: L2, L3, L4
obturator nerve: L2, L3, L4
lateral cut. nerve of thigh: L2 & l3
femoral nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
what movement does this cause? [2]
main muscles of anterior [3]
femoral nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
anterior
what movement does this cause? [2]
flex hip
extend knee
main muscles for ^?
quadriceps
sartoruis
iliopsoas