The Hip Flashcards
(38 cards)
which joint connects the pelvis to the sacrum? [1]
what is the name for the joint between L5 & sacrum? [1]
which joint connects the pelvis to the sacrum? [1]
sacro-iliac joint
what is the name for the joint between L5 & sacrum? [1]
lumbosacral joint



explain what is meant by the sacoiliac joint being a compound synovial joint [2]
explain what is meant by the sacoiliac joint being a compound synovial joint [2]
- *- anterior synovial plane joint**
- *- posteiror syndesmosis joint (**A syndesmosis is defined as a fibrous joint in which two adjacent bones are linked by a strong membrane or ligaments). stable joint !!
anteriorly, the left and right os coxa join together where? [1]
anteriorly, the left and right os coxa join together where? [1]
pubic symphysis
what are the three parts of the pelvic bone?


which part of pelvic bone do you sit on? [1]
which part of pelvic bone do you sit on? [1]
ishial tuborisity





A: ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine)
B: pubic tubercle
C: PSIS
D: ischial spine
E: ischial tuborisity
F: inferior pubic ramus

the hip joints is an articulation between? [2]
what movements does the hip joint do? [5]
the hip joints is an articulation between? [2]
- femoral head & acetabulum
what movements does the hip joint do? [5]
flexion, extension
abd, add,
lateral and medial rotation
circumduction
Hip stability is due to: ? [7]
- Deep insertion of femoral head into acetabulum
- Strong tight articular capsule, this is loose in shoulder. Attaches to greater trochanter and neck of the femur, so is a very tight fit. Gives stability yet also restricts movement
- Ligaments around the joint capsule (especially anteriorly) which will help stabilise the hip joint in extension (the anterior ligaments).
- Large powerful muscles around joint: single, individual most powerful muscle in the body is the gluteus maximus, and the most powerful group of muscles (quadriceps) all work to stabilise the hip joint
- Ligament within articular capsule, ligamentum teres. This attaches the head of the femur to the acetabulum and acts as like a tether. Can also be called ‘ligament of the head of the femur’.
- Fat pad fills central region and adds cushioning for thinnest part of acetabulum. Also helps to keep these two bones together
- Acetabulur labrum is a fibrocartilaginous ring that helps with suction of the femur into the acetabulum. Doesn’t really add to the surface area, 10%, but acts with the synovial fluid to suction the head of the femur into the acetabulum
where in the articular capsule of hip joint is strongest & thickest? [1]
where in the articular capsule of hip joint is thinnest and weakest? [1]
where in the articular capsule of hip joint is strongest & thickest? [1]
upper and anterior parts
where in the articular capsule of hip joint is thinnest and weakest? [1]
lower and posterior parts

which is the strongest ligament around the hip joint articular capsule, which strengthens the joint? [1]
which is the strongest ligament around the hip joint articular capsule, which strengthens the joint? [1]
- anterior iliofemoral ligament - makes anterior side more stable than posterior


when the hip is extended, what happens to the ligament fibres? [1]
what does this do the the femur & acetabulum? [1]
when the hip is extended, what happens to the ligament fibres? [1]
- fibres become twisted and extended (& tighten)
what does this do the the femur & acetabulum? [1]
ligaments pull head of femur & acetabulum closer

role of the acetabular labrum? [1]
structure of acetabular labrum? [1] - what makes rest of this? [1]
role of the acetabular labrum? [1]
deepens the socket - stabilises the joint more
structure of acetabular labrum? [1] - what makes rest of this? [1]
C shaped - rest is connect by transverse acetabular ligament

ligamentum teres of acetabulum - location? role?
ligamentum teres of acetabulum - location?
runs from acetabulum to the femoral head
ligamentum teres of acetabulum - role?
stabilises the joint

* the hip joint is most stable is which position ? *
* the hip joint is most stable is which position ? *
extension !
what position are people sitting in for hip dislocation most likelto occur in?
occurs when sitting in flexion and forces pushes head of femur posteriorly, out of acetabulum
posterior hip discolation can lead to WHICH nerve injury? [1]
what does this ^ present as? [3]
posterior hip discolation can lead to WHICH nerve injury? [1]
sciatic nerve
what does this ^ present as? [3]
foot drop
loss of achilles reflex
muscle wasting of hamstring
in order to elicit hip flexion, where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
in order to elicit hip extension, where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
in order to elicit hip adduction, where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
in order to elicit hip abduction, where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
in order to elicit hip medial rotation , where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
in order to elicit hip lateral rotation, where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
in order to elicit hip flexion, where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
anteriorly
in order to elicit hip extension, where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
posterioly
in order to elicit hip adduction, where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
medially
in order to elicit hip abduction, where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
laterally
in order to elicit hip medial rotation , where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
around hip joint
in order to elicit hip lateral rotation, where will the muscles of hip joint be? [1]
around hip joint


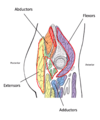
which is the major extensor muscle of the hip? [1]
which are the major abductor muscles of the hip? [2]
which are the lateral rotators muscles of the hip? [2]
which is the major extensor muscle of the hip? [1]
gluteus maximus
which is the major abductor muscles of the hip? [2]
gluteus medius and minimus
which are the lateral rotators muscles of the hip? [2]
piriformis and lateral rotators

during locomotion, which muscles stabilise the hip? [2]
how? [1]
during locomotion, which muscles stabilise the hip? [2]
gluteus medius and minimus: contract to keep pelvis aligned during locomotion (otherwise, get contralateral (hip drop)





















