Parasites of the Cardiovascular System Flashcards
(38 cards)
Canine and feline nematodes
Heartworm - Dirofilaria immitis
Size and lifespan of adult heartworm - Dirofilaria immitis (3)
- Females: ~25 cm long
- Males: ~15 cm long
- Live up to 7.5 years in dog
Microfilaria (3)
•Larval stage of Dirofilaria immitis - infectiuous stage, circulate canine blood
•~ 300 µm long
µm long
•Dogs can be patent for 5 years
Wolbachia endosymbiont (5)
- Intracellular bacterium, found in many filarial worms
- Mutualistic or symbiotic relationship
- Harboured by all stages of Dirofilaria immitis
- Required for fertility, survival & development of D. immitis
- Role in pathogenesis unclear - offers potential therapeutic target of ABs
Life cycle of Dirofilaria immitis (8)
- 1). Mosquito bites (vectorborne worm infection) infected dog and ignests larvae (L1).
- 2). Within the mosquito - larvae mature from L1 into L3.
- 3). Infected mosquito bites a healthy dog and transmits larvae (L3) to the dog’s subcutaneous tissues.
- 4). Larvae mature from L3 into L4 and infest the muscles and blood vessels.
- 5). Larvae mature into adult worms and infest the pulmonary artery and right heart.
- 6). Adult worms ate and produce larvae (L1) that are released into the blood (microfilaria)
- Dog = primary definitive host - maturation and reproduction
- Mosquito = intermediate host - where development occurs + vector

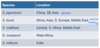
Reservoirs of Dirofilaria immitis (2)
- Wild canids - coyotes in USA
- Red foxes in Europe
PPP (pre-patent period) of Dirofilaria immitis
Greater than or equal to 6 months, time dog is infected to seeing microfilaria in bloodstream
What are the intermediate hosts of Dirofilaria immitis? - Species (3)

Geographical distribution of Dirofilaria immitis

What are the drivers for the spread of Dirofilaria immitis? (4)
- Global warming - climate change - warmer = inc in mosquito vectors (25-27 degrees Celcius), mosquitoes lay eggs in water bodies
- Movement of pets - cats and dogs - bring infection to non-endemic areas
- Biting behaviour of mosquitoes (exophilic to endophilic) - more likely to live indoors rather than outdoors
- Urbanisation of vector - where higher dog density = inc in transmission
What does the pathogenesis of Dirofilaria immitis depend on? (7)

Pathogenesis of Dirofilaria immitis in pulmonary arteries (5)
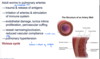
Pathogensis of Dirofilaria immitis - long-term sequelae (2)

What is the pathogenesis of severe cases with Dirofilaria immitis? (2)

Clinical signs - dogs, lighter infections (2)
- Asymptomatic
- Sustained exercise
Clinical signs - heavier infections - dogs (3)
- Loss of condition & exercise intolerance
- Chronic cough, shortness of breath
- Oedema & ascites
What are the clinical signs of vena cava syndrome in dogs with Dirofilaria immitis? (4)
- Haemoglobinuria
- Jaundice
- Collapse
- May be fatal
Dirofilaria immitis in cats - facts (5)

What is HARD (heartworm associated respiratory disease)? - Cats (3)

What is chronic feline heartworm disease? (3)

How is Dirofilaria immitis diagnosed? (9)

Prevention and control of Dirofilaria immitis (4)

Vector control of Dirofilaria immitis (3)

Is Dirofilaria immitis resistant to chemoprophylaxis? (6)