STEEPLECHASE - MUSCULOSKELETAL Flashcards
(186 cards)
1
Q

A
Brachygnathia
2
Q

A
Complete palatoschisis
3
Q

A
Prognathia
4
Q

A
Pectus excavatum
5
Q

A
Kyphosis
6
Q

A
Scoliosis
7
Q

A
Block vertebrae
8
Q

A
Butterfly/hemivertebrae
9
Q

A
Lordosis
10
Q

A
Manatee - confined in small aquarium, developed severe scoliosis (lateral deviation)
11
Q

A
Spina bifida in dog
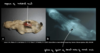
12
Q

A
Mircomelia
13
Q

A
Peromelia
14
Q

A
Notomelia
15
Q

A
Hemimelia
16
Q

A
Amelia
17
Q

A
Polydactyly
18
Q
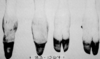
A
Syndactyly
19
Q

A
Ectrodactyly
20
Q

A
Dactylomegaly
21
Q

A
Adactyly
22
Q

A

23
Q

A
Osteogenesis impefecta - lateral deviation in joints, collagen I mutation
24
Q

A
Osteogenesis imperfecta

25
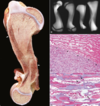

26

Osteopetrosis
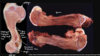
27


28
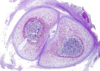
Congenital cortical hyperostosis

29

Congenital hyperostosis

30

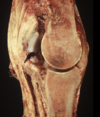
'Lion jaw' craniomandibular osteopathy
31

Craniomandibular osteopathy 'Lion jaw'
32

Chondrodysplasia

33
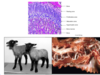

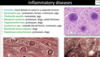
34

Disproportionate dwarfism - Grey alpine calf w/ Ellis van Creveld syndrome (chondrodysplasia)
35

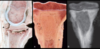
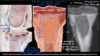
Manganese deficiency, not congenital, acquired/nutritional deficiency (chondrodysplasia)
36

Texel lamb - disproportionate dwarfism, shortened limbs and wide base (chondrodysplasia)
37

(Chondrodysplasia)
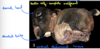
38

Osteochondrosis
39

Osteochondrosis latens - well-demarcated area of necrosis of cartilage
40

Osteochondrosis manifesta - arrows = associated with areas of foci of necrosis - areas of retained cartilage = hypertrophic chondrocytes
41
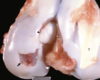
Osteochondrosis dissecans - arrow pointing to 'joint mice'
42

Vertebral myelopathy

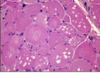
43

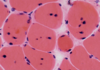
Dynamic vertebral myelopathy - flexion

44


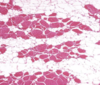
45
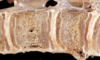
Osteoporosis

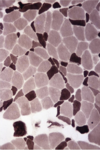
46

Rickets and osteomalacia
47
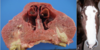

48

Head brachygnathia superior
49

Dental dysplasia, with small pink-grey barely erupted teeth in a two-week old Holstein calf with osteogenesis imperfecta (right), left = normal calf
50
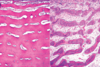

51

Osteopetrosis
52

Cervical vertebral myelopathy "Wobbler syndrome"
53
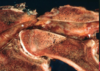
Cervical vertebral malformation-malarticulation in a horse. Flexion of the cervical vertebrae results in stenosis of the spinal canal (asterisk). Flaring of caudal epiphysis (arrowhead), can also contribute to spinal compression
54

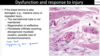
Cervical vertebral malformation-matriculation in a horse, Osteochondrosis of the articular facet joints can contribute to the intervertebral joint instability
55
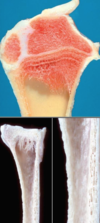
Osteoporosis
56

Osteoporosis
57

Osteoporosis
58

Osteoporosis
59

Costochondral junction, rickets
60
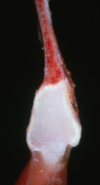
Pig, rib, dysplasia
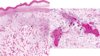
61
Fibrous osteodystrophy, "Rubber jaw"
62

Fibrous osteodystrophy
63
Fibrous osteodystrophy
64

Fibrous osteodystrophy
65


66


67


68


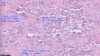
69
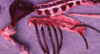
Congenital porphyria
70

Porphyria
71

Erythropoietic porphyria
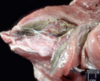
72
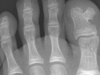
Exostosis
73

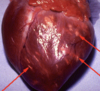
Enostosis
74
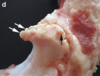
Osteophyte
75

Enthesophyte
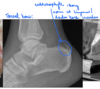
76

Hyperostosis
77

Hypertrophic osteopathy
78

Bone, hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy
79


80
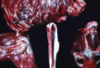
Osteochondromatosis feline leucopenia
81
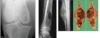
82

Subchondral cyst
83

Compression force
84

Avulsion/distraction forces
85

Shear forces @ mid diaphysis
86

Bending forces - two forces opposed to mid-diaphysis
87

Torsion force - twisting on longitudinal axis
88

Compound FX
89

Transverse FX - perpendicular to long axis of bone
90

Linear FX - parallel to long axis
91
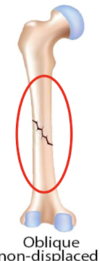
Oblique non-displaced - tangential (along), remain relatively aligned
92

Oblique displaced FX
93

Spiral 3D FX
94

Greenstick FX - cortical bone, minimal involvement of underlying trabeculae bone
95

Comminuted FX - severe forces (shatter FX fragments)
96


97
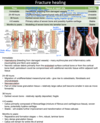

98

Direct or contact healing

99
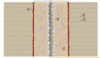
Small gap healing
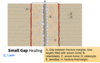
100


101

Thorax gunshot perforations
102

FX fixation devices - wires, screws, plates + intramedullary nails
103

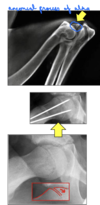
Epiphysiolysis - dog
104

Valgus deformity - deviation of limb laterally, damage on lateral aspect
105

Varus deformity - deviation of limb medially, damage occurred on medial aspect of physis
106
Sesamoid FX
107

Sesamoid FX
108

109

Chronic pyogranulomatous osteomyelitis in cow - Actinomyces bovis = lumpy jaw
110

Sequestrum in a foal with Salmonella osteomyelitis
111

Suppurative vertebral osteomyelitis in pig, usually Streptococcus suis
112

Highly suggestive histologic feature = Splendore-Hoeppli phenomenon (intense eosinophilic material)
113


114


115
116


117


118
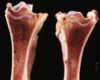
Bone osteomyelitis physis
119

Bone abscess
120

Large dog breeds

121

Panosteitis in a German Shepherd dog. Patchy foci of increased bone density within the medullary cavity (arrows)
122
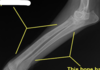
Panosteitis

123


124

Aseptic necrosis
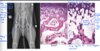
125

Cachexia (atrophy)
126

Muscle atrophy
127

Hyperadrenocorticism (Cushing's) - 'pot belly' due to abdominal muscle atrophy
128
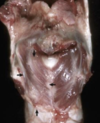
Left superficial cricoarytenoideus dorsalis muscle in horse - denervation atrophy
129

Compensatory response to injury

130
Vacuolar change
131
Internal nuclei
132

Whorled and ring fibres
133

134

Distinct groups of atrophic and hypertrophic fibres in child w/ spinal muscular atrophy, hypertrophic fibres up to 100 micrometres
135
Atrophy restricted to darkly stained type 2 fibres induced by steroid therapy
136

ATPase staining following preincubation at pH 4.3 showing atrophy selectively affecting darkly stained type 1 fibres in a case of myotubular myopathy + hypertrophy of pale type 2 fibres
137

Internal nuclei (arrow) within fibres of varying size, Duchenne muscular dystrophy
138

Chain of internal nuclei in longitudinally sectioned fibre 48 micrometres in diameter
139

An area of multiple splitting = small cluster of fibres
140

Hypertrophic fibres w/ multiple internal splits - Duchenne muscular dystrophy, small arrow = nuclei along splits, variation in fibre size due to branching of fibres (large arrow)
141

Whorled fibre w/ twisted myofibrils
142


143


144
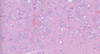
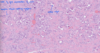
145

Segmental necrosis
146

Segmental necrosis

147
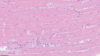
Segmental necrosis

148
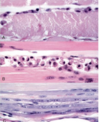
Muscle necrosis and regeneration
149

Muscle regeneration - myotubule grows + differentiates + develops sarcomeres (striation) and nuclei move to the periphery (requires intact basal lamina)
150

151

152
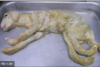
Arthrogryposis - failure of innervation of muscles
153

Hypermuscular Belgian blue bull
154

Splay leg in pigs, myofibrillar hypoplasia
155


156

Muscle dystrophy
157

Myotonia (channelopathies) - inability of skeletal muscle to relax
158


159

Splay leg syndrome
160

Muscle - lumbar porcine stress syndrome, malignant hyperthermia

161


162

163

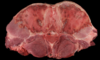
Degenerative myopathy - disturbance of circulation -\> saddle thrombus

164

Degenerative myopathy - disturbance of circulation

165


166

Ischaemic muscle necrosis - cow
167

Rear leg muscle - coagulative necrosis of cow
168


169

White muscle disease, selenium and vit E deficiency
170
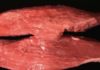
White muscle selenium deficiency
171
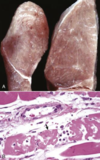
Toxic myopathy - monophasic/polyphasic necrosis
172


173
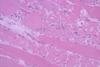
Myodegeneration - cassia toxicity
174
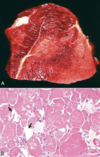
Exertional myopathy
175

Exertional myopathy or 'capture myopathy' in wild animals
176

Traumatic diaphragmatic hernia
177

Myositis ossificans

178

Suppurative myositis
179

Inflammatory diseases

180

Clostridium chauvoei, clostridial myositis
181
Pyogenic bacteria, localised suppurative + necrotising myositis - injection site in a cow
182

Inflammatory disease

183

184
FMDV - pale multifocal, irregular, linear stripping (piglet)
185

186




