STEEPLECHASE - NERVOUS SYSTEM Flashcards

Taenia multiceps (tapeworm) - with double ring of rostellar hooks

Cestode - proglottids

General cestode adult morphology, segmented

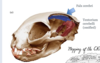
Taenia multiceps cyst (coenurus) in sheep brain


Coenurus cyst on left cerebral hemisphere in 6 m/o lamb

General appearance of taenia/echinococcus eggs

Thelazia - nematode

Thelazia callipaeda


Muscid fly - Thelazia vector

Clinical signs of Thalezia - eye lesions - cloudy and ulcerated cornea, ulcerated eye

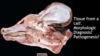
Surface and cut views of cerebrum of 20 y/o Paint horse with histologically confirmed EPM (equine protozoal myeloencephalitis, due to Sarcocystis neurona)

Sciatic nerve





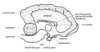

Dog, transverse slice - grey mass on floor of right ventricle

Dog, transverse slices, asymmetric ventricle dilation

(Representative samples taken from brain)


Frontal lobe/basal nuclei

Thalamus

Thalamus
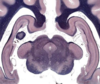
Midbrain

Pons

Brainstem/cerebellum