STEEPLECHASE - Special Senses EAR Flashcards
(141 cards)

Otodectes cynotis

Otodectes cynotis

Demodex canis

Demodex canis / cati

Sarcoptes scabiei var. canis - mites found on deep skin scrapes - burrowing mite

Sarcoptes scabiei var. canis - mites found on deep skin scrapes - burrowing mite



Foreign body

Acute atopy

Acute atopy

Chronic atopy

Chronic atopy

Cutaneous adverse food reaction (CAFR)

Contact hypersensitivity - erythema often seen dorsally and ventrally to external acoustic meatus (where medication is common in contact w/ skin of ear)



Keratinisation disorders - endocrine disease (hypothyroidism, hyperadrenocorticism, sex hormone dermatoses); sebaceous adenitis; primary idiopathic seborrhoea





Feline ceruminous cystomatosis




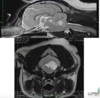
Feline nasopharyngeal (inflammatory) polyp - non-neoplastic feline ear mass

Feline nasopharyngeal (inflammatory) polyp - non-neoplastic feline ear mass