Infection and Inflammation of the CNS Flashcards
Defence mechanisms in the brain (4)

What are the different routes of infection + examples? (4)

General features of lesions and the nature of the infecting organism (4)

Suppurative inflammation - bacterial? fungal/algal/protozoan/helminth? viral? non-infectious agents?
Bacterial = Listeria, embolic diseases, septicaemias
Fungal/algal/protozoan/helminth = Aspergillus, Amebae, Prototheca, Encephalitozoon cuniculi
Viral = arbovirus
Eosinophilic inflammation - bacterial? fungal/algal/protozoan/helminth? viral? non-infectious agents?
Fungal/algal/protozoan/helminth = Helminths (coenurus, cysticercus)
Non-infectious = allergy?
Suppurative-pyogranulomatous inflammation - bacterial? fungal/algal/protozoan/helminth? viral? non-infectious agents?
Fungal/algal/protozoan/helminth = Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum, Cryptoccocus neoformans, Sarcocystis neurona
Non-suppurative inflammation (lymphocytes + plasma cells) bacterial? fungal/algal/protozoan/helminth? viral? non-infectious agents?
Viral = Rabies, Aujeszky, Distemper, EEE, VEE, JEE, EHV*, West Nile, Borna
Non-suppurative/granulomatous inflammation - bacterial? fungal/algal/protozoan/helminth? viral? non-infectious agents?
Bacterial = mycobacteria
Viral = Visna-maedi, CAEV, EIAV, FIP
Non-infectious agents = GME = granulomatous meningoencephalitis, NME = necrotising meningoencephalitis
Grey matter inflammation (polio) - bacterial? fungal/algal/protozoan/helminth? viral? non-infectious agents?
Viral = Rabies, Aujeszky, EEE, VEE, JEE, EHV*, West Nile, Borna
Non-infectious = NME = necrotising meningoencephalitis
White matter inflammation (leuko) - bacterial? fungal/algal/protozoan/helminth? viral? non-infectious agents?
Viral = Distemper, Border disease, Visna-Maedi
Non-infectious = GME = granulomatous meningoencephalitis
Vasculitis - bacterial? fungal/algal/protozoan/helminth? viral? non-infectious agents?
Bacterial = TME = thrombotic meningoencephalitis
Viral = FIP, herpesviruses, CSF, ASF, MCF
What do bacterial infections involve and the common patterns associated with inflammation (7)

What is meningitis? species, bacteria, portal of entry, clinical signs (13)


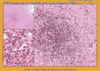
Diffuse suppurative meningitis - pig


Suppurative meningitis

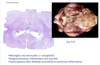
What are cerebral abscesses? (2)

Cerebral abscesses - haematogenous location (2)