2.5.1 GI Development Flashcards
(46 cards)
What are the two parts of the anal canal?
Hindgut endoderm
— pecinate line —
Anal pit ectoderm

What acts as the axis of the first primary loop of the midgut?
SMA
What are the hindgut derived GI segments?

Differental growth causes expansion of the stomach into what?
Dorsal mesentary
What are the 6 midgut derived organs?
- Distal half (3rd and 4th) of the duodenum
- Jejunum
- Ileum
- Cecum and appendix
- Ascending colon
- Proximal 2/3 of the transverse colon

What two extraembryonic structures provide additional features the the primitive gut tube?
yolk sac and allantois
What does the SMA supply blood to?
Midgut and its derivative organs
The ventral mesentary forms from the lower portion of the septum transversum. What structures will this give rise to?
Future lesser omentum and falciform ligament
What this be?

Hirschsprung Dz
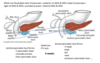
What might this be?

Annular pancreas (1 in 15,000)
What are the three phases of midgut development?
- Elongation, herniation, and rotation (90)
- Return to the abdominal cavity and rotation (180)
- Fixation of the mesentaries
What this be?

Imperforate anus

Identify these two structures

Left: yolk sac
Right: allantois
What is the classical sign of duodenal atresia on x-ray?
“Double bubble sign”
Also, seen with annular pancreas

The foregut endoderm proliferates to form buds for what three organs?
liver, gall bladder, and pancreas
What does the dorsal pancreatic bud give rise to?
Future minor duodenal papilla
Identify this conditon

Pyloric stenosis
What are some early derivatives of the foregut?
esophagus, stomach, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, 1st and 2nd portions of the duodenum
Meckel’s diverticulum leads to what two symptoms?
Intussesception and pain
What this be?

Gut rotation abnormalities
How is omphalocele most commonly detected and diagnosed?
Prenatal ultrasound (or AFP/apha-fetoprotein screening)
Identify

Top: Ventral mesentary
Bottom: Dorsal mesentary
Identify these structures


What this be?

Meckel’s diverticulum