Multisystem Flashcards
Mechanism of Amanita phalloides mushroom poisoning
Inhibition of RNA polymerase II
smooth endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for…?
Site of steroid synthesis and detoxification of drugs and poisons. Lacks surface ribosomes.
-Liver hepatocytes and steroid hormone– producing cells of the adrenal cortex and gonads are rich in SER
Pellagra is a syndrome of what and what are the sx?
Vitamin B3 (niacin) deficiency
-Diarrhea, Dementia (also hallucinations), Dermatitis (C3/C4 dermatome circumferential “broad collar” rash [Casal necklace], hyperpigmentation of sun-exposed limb
Positive charged AA
Lysine, Histadine, Arginine

What are the rate limiting steps of:
- Glycolysis
- TCA cycle
- Gluconeogenesis
- Glycogenesis
- Glycogenolysis
- HMP Shunt
- De Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis
- De Novo Purine Synthesis
- Urea Cycle
- Ketogenesis
- Cholesterol Synthesis
- Glycolysis: Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
- TCA cycle: Isocitrate dehydrogenase
- Gluconeogenesis: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
- Glycogenesis: Glycogen synthase
- Glycogenolysis: Glycogen phosphorylase
- HMP Shunt: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)
- De Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II
- De Novo Purine Synthesis: Glutamine-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP) amidotransferase
- Urea Cycle: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
- Ketogenesis: HMG CoA synthase
- Cholesterol: HMG CoA reductase
CYP450 Inducers
CRAP GPS’S induce me to CHRONIC madness!!
- *C**arbemazepines
- *Ri**fampicin (inhibits RNA polymerase in prokaryotes; TB)
- *A**lcohol (chronic)
- *P**henytoin (increase Na channel inactivation; seizures)
- *G**riseofulvin (inhibits growth of dermatophytes (tinea, ringworm)
- *P**henobarbital (barbituate, facilitate GABA-a)
- *S**ulphonylureas (T2 DM, close K channel)
St. John Wort
CYP450 Inhibitors
CRACK AMIGOS inhibit life
- *C**imetidine
- *R**itonavir (protease inhibitor)
- *A**miodarone
- *C**iprofloxacin
- *K**etocanazole (and other azoles)
- *A**cute alcohol use
- *M**acrolides
- *I**soniazid
- *G**rapefruit Juice
- *O**meprazole
- *S**ulfonamides
Essential Amino Acids

Nonessential Amino Acids that become essential during times of growth
Arginine and Histidine
Hyperammonemia
Can be acquired (e.g., liver disease) or hereditary (e.g., urea cycle enzyme deficiencies).
Results in excess NH4+, which depletes α-ketoglutarate, leading to inhibition of TCA cycle.
Tx: limit protein in diet. Lactulose to acidify the GI tract and trap NH4+ for excretion. Rifaximin to colonic ammoniagenic bacteria
Ammonia intoxication—tremor (asterixis), slurring of speech, somnolence, vomiting, cerebral edema, blurring of vision.
Friedreich ataxia
Autosomal recessive trinucleotide repeat disorder (GAA) on chromosome 9 in gene that encodes frataxin (iron binding protein). Leads to impairment in mitochondrial functioning. Degeneration of multiple spinal cord tracts muscle weakness and loss
of DTRs, vibratory sense, proprioception.
Presentation: Staggering gait, frequent falling, nystagmus, dysarthria, pes cavus, hammer toes, diabetes mellitus, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (cause of death). Presents in childhood with kyphoscoliosis
“Friedreich is Fratastic (frataxin): he’s your favorite frat brother, always staggering and falling but has a sweet, big heart”

Marfan Syndrome
FBN1 gene mutation on chromosome 15 defective fibrin (scaffold for elastin) connective tissue disorder affecting skeleton, heart, and eyes.
Findings: tall with long extremities, pectus excavatum, hypermobile joints, and long, tapering fingers and toes (arachnodactyly); cystic medial necrosis of aorta aortic, incompetence, and dissecting aortic aneurysms; floppy mitral valve.
-Subluxation of lenses, typically upward and temporally.

Lens subluxation downward and inward vs lens subluxation upward and temporally
downward and inward –> homocystinuria (down and inward, in SAME DIRECTION=HOMO)
upward and temporally –> Marfan syndrome (think looking up to the heavans or to MARS!)
McArdle disease (type V)
glycogen in muscle, but muscle cannot break it down painful muscle cramps, myoglobinuria (red urine) with strenuous exercise, and arrhythmia from electrolyte abnormalities
-Deficient Skeletal muscle glycogen phosphorylase (myophosphorylase)
-McArdle = Muscle
Treat with vitamin B6 (cofactor)
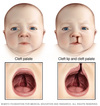
Cleft Lip vs Cleft Palate
Cleft lip—failure of fusion of the maxillary and medial nasal processes (formation of 1° palate).
Cleft palate—failure of fusion of the two lateral palatine processes or failure of fusion of lateral palatine processes with the nasal septum and/ or median palatine process (formation of 2° palate).