L13- Bone introduction Flashcards
bone is a type of
connective tissue
how many types of bone in the body
5
name the 5 types of bone in the body
1) long bones 2) short bones 3) flat bones 4) irregular bones 5) sesamoid
long bones
• Longer than wide • Function: support weight of the body and allow movement • e.g. Humerus, small bones in fingers
short bones
• As long as they are wide • Function: short bones provide stability and some movement • e.g. Trapezoid, wrist (carpals) bone, ankle (tarsals)
flat bones
• Flattened, with parallel edges • Function: protects internal organ- large area of attachment for muscle • e.g. Sternum and ribs , cranial bones, pelvis
irregular bones
• Vary in shape and structure (complex shape) • Function: protect internal organs • e.g. Vertebra protect spinal cord • e.g. Pelvis (sacrum) protects organs in the pelvic cavity
sesamoid (sesame like)
• Embedded in tendons • Function: protect tendons from stress and damage from repeated wear and tear • e.g. small round bones found in the tendons of the hands, knees and feet - Patella is a good example- forms postnatally
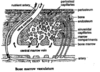
outer most layer of bone is called the
periosteum
inner portion of the bone called
cancellous or spongy bone
features of cancellous/ spongy bone
- Strong - Light - Filled with bone marrow (trabeculae)
outer portion (external surface) of bone
compact bone
features of compact bone
80% of bone mass - Much more dense than cancellous bone o Fewer spaces
organisation of compact
Compact bone is tightly organised into osteons
osteons
Osteons are formed by layers of lamellae that wrap around each other.