BIOC 202 - Sugars and Others Flashcards
(21 cards)
What is it and to what AA(s) is it done to?
Phosphorylation
Adding phosphate to an -OH
Ser, Tyr, Thr
What is it and to what AA(s) is it done to?
Glycosylation
Addition of sugars
Ser, Thr, Tyr -> O-Glycosylation ( -OH group)
Arg, Asn -> N-Glycosylation (N-)
What is it and to what AA(s) is it done to?
Hydroxylation
Adding a hydroxyl group (-OH)
Proline -> hydroxyproline
What is it and to what AA(s) is it done to?
Carboxylation
Addition of carboxyl group
Glutamate (for blood clotting)
What is it and to what AA(s) is it done to?
Acetylation
Attachment of acetyl group
Lysine (regulation of gene expression, i.e. epigenetics)
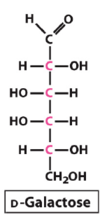
Draw and name the linear structure of the sugar below
D-Glucose

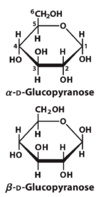
Draw and name the cyclic structure of the sugar below
D-Glucose
(any Anomer)
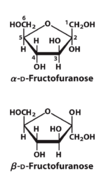
Draw and name the linear structure of the sugar below
D-Fructose

Draw and name the cyclic structure of the sugar below
D-Fructose
Draw and name the linear and cyclic structures of the sugar below
D-Galactose
Draw and name the cyclic structure of the sugar below
D-Galactose
(Any anomer)

Why is ATP hydrolysis favourable? (4 reasons)
1) Relief of charge repulsion (-4 → -3 when going from ATP to ADP)
2) Resonance stabelization of phosphate (the one that comes off)
3) Ionization of ADP (multiple ionization states increase ADP entropy, which makes ADP formation more entropically favoured)
4) Greater solvation of products (more H-bonds can be formed)

Draw Ribose and adenine (to make sure you recognize it right)
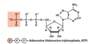
What is the main thing about ATP hydrolysis that drives reactions?
Phosphoryl transfer (NOT the hydrolysis)
What is creatine phosphate for?
To generate ATP in muscle during first few seconds of heavy muscle contractions
Creatine phosphate is “Creating phosphate” (memory aid)
What is the definition of a carbohydrate and what is the general formula?
An aldehyde or ketone compound with multiple hydroxyl-groups
General formula: (CH2O)n
Aldose vs. Ketose
Aldose is an aldehyde based sugar, ketoses is ketone based
Anomer vs. epimer
Anomer is a specific type of epimer, where there is a difference of only one chiral centre between stereoisomers
What proportions does glucose exist in within a cell? (ring and open chain forms)
1/3 a-ring
2/3 b-ring
< 1% open-chain
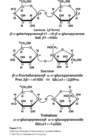
Draw Maltose, providing the specific name of the bond, the component monosaccharides, and the bond notation between monosaccharides

difference between -osyl, -oside, and -ose
- ose is for the second sugar in a linkage that does NOT involve the second sugar’s anomeric carbon
- oside is for the second sugar in the linkage that DOES involve the second sugar’s anomeric carbon
- osyl is for the first sugar in a glycosidic bond (to indicate that particular sugar is the anomer reacted)