Unit 7 Pt. 1 (PD Complex) Flashcards
(27 cards)
What converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH complex)
Where in the cell is the PDH complex located?
In the mitochondrial matrix
What is the overall reaction of the PDH complex?
Pyruvate is decarboxylated (and oxidized) into acetate, followed by the formation of acetyl-CoA (a thioester)
*note that free acetate never actually forms

What is E1 of the PDH?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
What is e2 of PDH?
Dihydrolipoyltransacetylase
What is E3 of the PDH?
dihydrolipoyldehydrogenase
What are the cofactors involved with the PDH complex and where are they found?
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) - bound to E1
Lipoamide/lipolysine - bound to E2
FAD - Bound to E3
NAD+ - Free
CoA(SH) - Free
What molecules make up Coenzyme A?
ADP, Vitamin B5 (pantothenate) and ß-mercaptoethylamine
What is the function of acetyl-CoA?
Carries the acyl group by forming a high energy thioester bond. “Primes” acetate for metabolism.
What is TPP?
Thiamin pyrophosphate
What is thiamin pyrophosphate derived from?
Derived from vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
What is special about TPP?
It can easily form a reactive carbanion
What is this molecule?


What is this molecule?

Coenzyme A

What is lipoic aside attached to?
It is attached to a lysine side chain on E2, forming lipoylysine
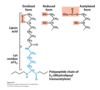
What is the function of lipoylysine?
Oxidizes hydroxyethyl to acyl groups and attaches in to one of the two sulphur atoms on lipoic acid (breaks disulphide bridge in process)
Acts as a “robotic arm” that carries acetyl group between reactions
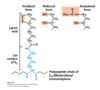
What is the first step of the PDH mechanism?
TPP carbanion attacks pyruvate and decarboxylates it, forming the hydroxyethyl-TPP intermediate

What is the second step of the PDH mechanism?
2a) Lipoylysine from E2 swings toward E1
2b) Hydroxyethyl-TPP group is oxidize to acetyl group and transferred to lipoylysine arm
What is the third step of the PDH mechanism?
3a) Lipoylysine arms swings into E2
3b) Acetyl group is transfered to CoASH, forming Acetyl-CoA. Lipoylysine become reduced in the process
3c) Acetyl-CoA leaves PDH complex
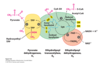
What is the fourth step of the PDH mechanism?
4a) Lipoylysine arms swings to E3
4b) Lipoylysine arm gets oxidized (specifically, the lipoic acid) by FAD, reducing it to FADH2
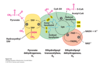
What happens in step 5 of the PDH mechanism?
NAD+ enters E3 and oxidizes FADH2 back into FAD. NAD+ gets reduced to NADH + H+ and leaves E3

How does Acetyl-CoA affect the PDH complex?
It will INHIBIT E2 (product inhibition)
How does NADH affect the PDH complex?
Will inhibit E3 (Product Inhbition)
Where does the majority of PDH complex regulation occur, and how?
On E1; through phosphorylation