Unit 7 - Kreb Cycle Flashcards
(23 cards)
Enzyme used for reaction 1 of the Kreb Cycle?
Citrate Synthase

Products of reaction 1 of the Kreb Cycle?
Citrate, CoA-SH (Coenzyme A)

What is a synthase?
Enzyme that catalyzses SYNTHESIS reactions without ATP or GTP
What is a synthetase?
Same as synthase, but directly requires ATP or GTP
What happens in reaction 1 of the Kreb Cycle?
Acetyl-CoA & Oxaloacetate form Citrate

What happens in reaction 2 of Kreb Cycle?
What drives reaction 2?
Citrate reversibly forms isocitrate from citrate
Driven by irreversibility of steps 1 and 3

Enzyme used in reaction 2 of Kreb Cycle?
Aconitase

What happens in step 3 of Kreb cycle?
Reversibility?
Isocitrate is irreversibly oxidized & decarboxylated to alpha-ketoglutarate irreversibly
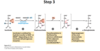
Enzyme used in step 3 of Kreb cycle?
Isocitrate dehydrogenase

Products formed in step 3 of Kreb cycle?
Alpha-ketoglutarate, NADH, and CO2 (from oxaloacetate, not the acetyl-coa component)
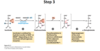
What happens in step 4 of Kreb cycle?
Revesibility?
α-ketoglutarate (bound to CoASH) is oxidized & decarboxylated to succinyl-CoA
Irreversible

Enzyme used in step 4 of Kreb cycle?
Products?
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenzse complex
Succinyl-CoA, NADH, CO2 (from oxaloacetate again, like in step 3)

By what mechanism does the α-ketoglutarate complex follow?
Essentially the same as the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, with thiamine pyrphosphate, lipoyllysine oxidation and reduction, and the dehydrogenase of lipoyllysine using NAD+
What happens in step 5 of kreb cycle?
REversibility?
Succinyl-CoA is converted to succinate reversibly

Enzyme used in step 5 of kreb cycle?
Products?
Succinyl-CoA Synthetase (*named after reverse reaction)
GTP, CoA-SH

What happens in step 6 of kreb cycle?
Reversibility?
Succinate is reversibly converted to fumarate

Enzyme used in step 6 of kreb cycle?
Products?
Succinate dehydrogenase
FADH2, Fumarate

What happens in step 7 of Kreb cycle?
Reversibility?
Fumarate reversibly converted to L-malate

Enzyme used in step 7 of Kreb cycle?
Products?
Fumarase (essentially adds water to C=C bond)
L-Malate

What happens in Step 8 of Kreb Cycle?
Reversibility?
Convert L-matae to oxaloacetate reversibly

Enzyme used in Step 8 of Kreb Cycle?
Products?
L-malate dehydogenase
NADH, Oxaloacetate
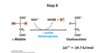
What is the overall reaction of Kreb cycle?

What molecules regulate Kreb cycle and at what steps?
*draw cycle, label regulators, and the type of regulation (where applicable)
Reaction 1 - Citrate Synthase
- Increase in NADH - INHIBIT
- Increase in ADP - activate
- Increase in citrate - INHIBIT (Product inhibition)
- Increase in ATP - INHIBIT
- Increase in Succinyl-CoA - INHIBIT (Feedback Inhibition)
Reaction 3 - Isocitrate dehydrogenase
- Increase in in ATP - Inhibit
- Increase in NADH - Inhibit
- Increase in ADP - Activate
- Increase in Ca2+ - Activate (muscle usage)
Reaction 4 - α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
- Increase in ATP - inhibit
- Increase in NADH - inhibit
- Increase in Succinyl-CoA - INHIBIT (Product inhibition)
- Incrase in Ca2+ - Activate



