Topic 6 ammen. - Fermentation and Glycolysis Regulation Flashcards
(30 cards)
What is the final electron acceptor in aerobic systems (and what is it reduced to? Show balanced chemical equation)?
Oxygen
2H+ + 2e- + 1/2 O2 → H2O
What is the function of electron carriers?
Carry and transfer e- and H+ to ETC and other reactions that require them
What is NAD and NADP?
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD)
NADP - Nicotinamidne Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate

Where is NAD and NADP derived from?
Derived from ATP and niacin (AKA vitamin B3)

What is the chemical and functional difference between NAD and NADP?
NAD has OH on ribose C-2; NADP has a phosphate instead on the same position
NADP is for catabolic (break-down) reactions, NADP is for anabolic (build-up) reactions (for regulatory reasons)

What is FAD and FMN?
FAD - Flavin Adenine Dinulceotide
FMN - Flavin MonoNucleuotide

Where is FAD and FMN derived from?
ATP and Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)

What is the chemical differences between FAD and FMN?
FMN lacks an AMP group
What is the key functional difference between FAD/FMN and NAD/NADP?
FAD/FMN are usually bound to something (ex. protein), whereas NAD/NADP are free to move around
How is NAD+ regenerated in aerobic systems (include final acceptor and carrier)?
ETC, where O2 is the final acceptor and H2O is the final carrier of electrons.
How is NAD+ regenerated in ANaerobic conditions?
No oxygen present, therefore FERMENTATION occurs.
Final electron donors and acceptors depend on type of fermentation carried out.
What type of fermentation occurs in mammals?
Lactate fermentation
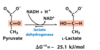
What enzyme catalyzes lactate fermentation, and is it reversible?
Lactate dehydrogenase, reversible

What happens in lactate fermentation? Name the final electron acceptors and carriers.
Pyruvate is reduced to lactic acid (lactate), reforming NAD+ in the process
Pyruvate is the final electron acceptor
Lactate is the final electron acceptor

What type of fermentation occurs in yeast?
2-step ethanol fermentation
What 2 enzymes catlyze ethanol fermentation, and what are their function?
Pyruvate decarboxylase (removes CO2 from pyruvate) and alcohol dehydrogenase (Reduces actetaldehyde and reforms NAD+)
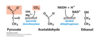
What happens in ethanol fermentation? List the electron final electron acceptor and carrier,
Pyruvate decarboxylated to form acetaldehyde, which is reduced to form ethanol (and regenerate NAD+)
Acetalaldehyde is the final electron acceptor, ethanol is the final electron carrier.
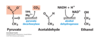
What is the function of fermentation?
To regenerate NAD+ to allow for the continuation of glycolysis in ANaerobic conditions
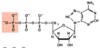
Name the following compound


Name the following compound

How is glycosylation regulated, and at which steps?
It is regulated at a CELLULAR level via alllosteric regulation (usually), and occurs in the 3 irreversible steps:
1) Hexokinase
3) PFK-1
7) Pyruvate kinase
How does ATP affect PFK-1?
It inhibits PFK-1 (indiates that there is an excess of ATP and that more pyruvates aren’t really needed)
How does an increase in AMP affect PFK-1?
It activates PFK-1 (indiates that there is an need for more ATP so more pyruvates are needed)
How does an increase in Fructose 2,6-biphosphate affect PFK-1?
Stimulates PFK-1 (this is hormone regulated; more later)


