Glycolysis Flashcards
(54 cards)
What are the 2 “stages” of glycolysis and their purpose?
Preperative stage & Payoff stage
Preparative - Trap and destabilize glucose, and cleavage of phophofructose by investing ATP
Payoff - ATP, NADH, and pyruvate are generated
By what method does glucose enter into the cell?
facilitated diffusion through glucose transporters
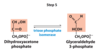
What happens in the first step of glycolysis?
Glucose is phosphroylated using ATP into Glucose 6-Phosphate (G6P)

What enzyme catalyzes the first reaction in glycolysis?
Hexokinase
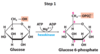
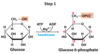
What substrates are used by hexokinase, and what are its products (in step 1 of glycolysis)?
Substrates: Glucose, ATP, Mg2+
Products: Glucose 6-Phosphate, ADP, Mg2+

What is the purpose of the first reaction in glycolysis?
To trap glucose in the cell (no transporter for phsophorylated glucose to “escape” through)
To destabilize glucose for further reatctions

Is hexokinase reversible?
No, irreversible
What is a kinase?
An enzyme that transfers a phosphoryl group from ATP to another molecule (or sometimes vice versa)
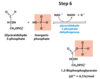
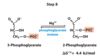
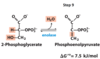
What happens in step 2 of hydrolysis?
Glucose 6-phopate (G6P) is isomerized into fructose 6-phosphate (F6P)

What enzyme catalyzes the second step of hydrolysis?
Phophohexose isomerase
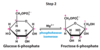
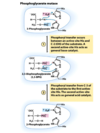
What is the mechanism for step 2 of glycolysis?
Multistep
- Open the ring to linear form
- Convert G6P → F6P
- Close ring to cylic form
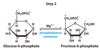
What are the substrate and products of the phosphohexose reaction in step 2 of hydrolysis?
Substrates: Glucose 6-phosphate (G6P) , Mg2+ (not consumed)
Product: Fructose 6-Phosphate (F6P)

Is phosphohexose isomerase reversible?
Yes (but recall it depends on ΔG, not ΔG0)

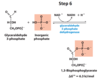
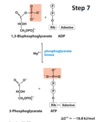
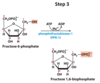
What happens in the third step of glycolysis?
Phosphorylation of Fructose 6-Phosphate → Fructose 1,6-biphosphate (F-1, 6-BP)
What enzyme catalyzes step 3 of hydrolysis?
Phosphofructokinase-1
(PFK-1)

What are the substrates and products used by phsphofuctokinase-1 in step 3 of hydrolysis?
Reactant: Fructose 6-Phosphate, ATP, Mg2+ (not actually consumed)
Product: Fructose 1,6-biphosphate, ADP

Is phosphofructokinase-1 reversible?
No, it is irreversible
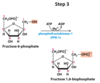
What is the rate-determening step of glycolysis?
Step 3; phosphorylation of Fructose 6-Phosphate. This is the “committed” step.
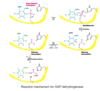
What happens in step 4 of hydrolysis?
Cleavage of F-1,6-P → dihydroxyacectonephosphate (DHAP) and Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate (G3P)

What enzyme catalyzes the step 4 of hydrolysis?
Aldolase
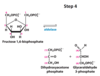
What are the substrates and products of aldolase in the 4th step of hydrolysis?
Substrate: Fructose 1,6-biphosphate
Product: Dihydroxyacteonephosphate (DHAP) and Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate (G3P)
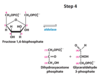
Is aldolase reversible?
Yes, reversible

What happens in step 5 of hydrolysis?
Conversion of DHAP → G3P

What is the purpose of step 5 in hydrolysis?
Convert DHAP into G3P because only G3P is used in phase 2 (“payoff phase”) of glycolysis